Figure 1.
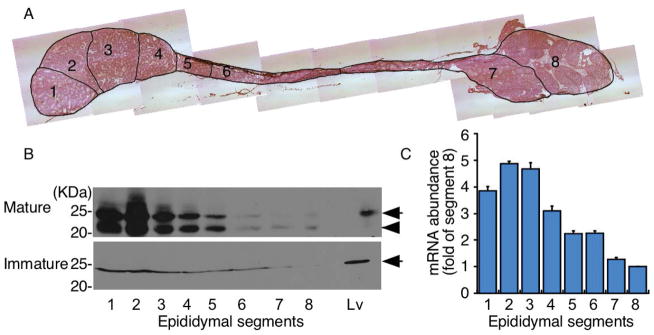
Characterization of epididymal cysteine deoxygenase (CDO) expression. (A) Histology of mouse epididymides collected from sexually mature mice showing segments 1–8. (B) Comparison of CDO protein expression in the epididymis of mature and immature (4-week-old) male mice. CDO in the liver (Lv) is shown for comparison [22]. Each lane was loaded with 100 μg epididymal proteins. Immunoblotting for CDO revealed that CDO expression (arrow) was abundant in segments 1–3 of the caput region, but was dramatically lower in subsequent segments towards the cauda region. Higher CDO expression was found in mature versus immature mice. CDO expression in mature mice was accompanied by the appearance of the non-cofactor (arrow) and cysteine-tyrosine cross-linked cofactor (arrow head) forms (B, top). In contrast, only the non-cofactor form of CDO was detected in immature mice (B, bottom). (C) CDO mRNA quantification in sections of epididymides from sexually mature mice was consistent with the high CDO expression level in the caput compared with that in the corpus and cauda regions. Data are means ± standard error (SE) of five independent replicates.