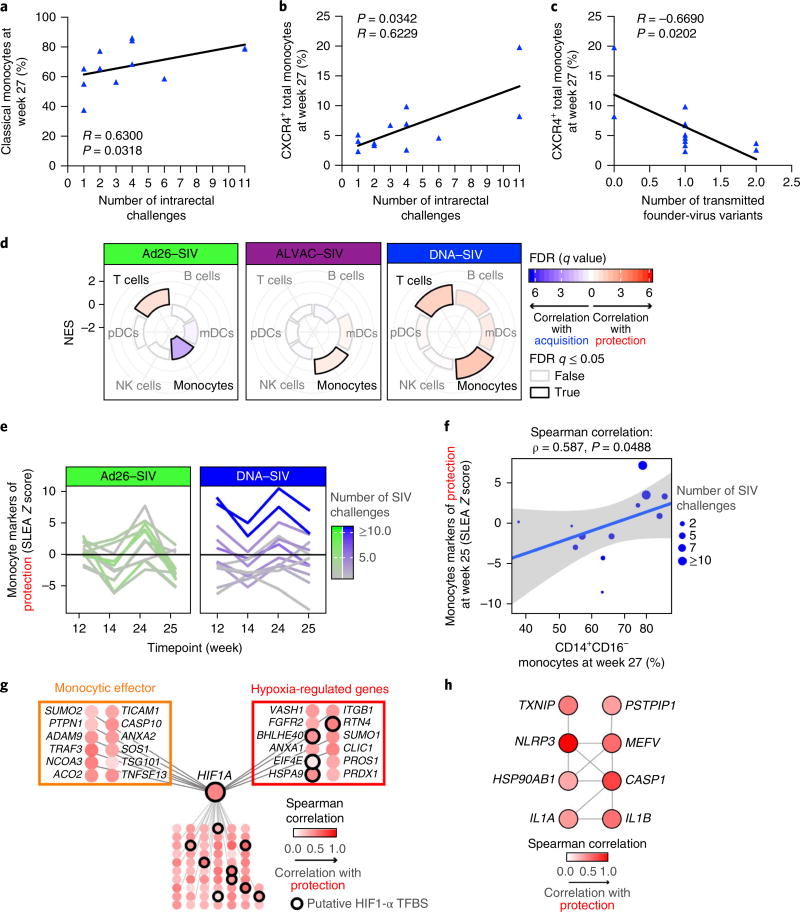
Fig. 2. Differential contribution of monocytes to protection.
a,b, The frequency of classical (CD14+CD16−) (a) and CXCR4+ (b) monocytes measured in the blood (week 27) in the DNA group correlates with the risk of SIVmac251 acquisition (the number of challenges to infection; n = 12). c, The frequency of CXCR4+ monocytes in the DNA group correlates with the number of transmitted SIV variants in the animals that became infected. A Spearman correlation was used for statistical analysis in a–c. d, Radial plots showing the relative contribution of immune subsets in protection against SIV acquisition. The normalized enrichment score (NES) estimated by GSEA is plotted for each subset and separated by vaccine regimen (Ad26–SIV: n = 11 animals, ALVAC–SIV: n = 27 animals and DNA–SIV: n = 12 animals). An NES of >0 or NES of <0 corresponds to markers of immune subsets enriched among genes associated with protection or SIV acquisition, respectively. FDR, false discovery rate; mDC, myeloid dendritic cell; pDC, plasmacytoid dendritic cell. e, Line plot showing the normalized average expression of monocyte genes associated with protection in each macaque (y axis) as a function of the four timepoints after boosting with ALVAC–SIV + gp120 (x axis) for both the Ad26–SIV (n = 11 animals) and the DNA–SIV (n = 12 animals) vaccine regimens. SLEA, sample-level enrichment analysis. f, Scatter plot showing the normalized average expression of monocyte genes associated with protection in each macaque at week 25 (y axis) as a function of the fraction of classical monocytes (CD14+CD16−) among monocytes at week 27 (n = 12 animals). The linear regression fit (blue line) and the 95% confidence interval (gray region) are given on the plot. g,h, The GeneMANIA network of the monocyte genes associated with protection from SIV challenge (g) and the network of the monocyte genes associated with protection from SIV infection that are part of the inflammasome pathway of REACTOME (h). TFBS, transcription factor–binding site. Each node is colored by the Spearman correlation of the genes (24 h after the second boost) with the number of SIV challenges to infection of the DNA–SIV animals (n = 12 animals).