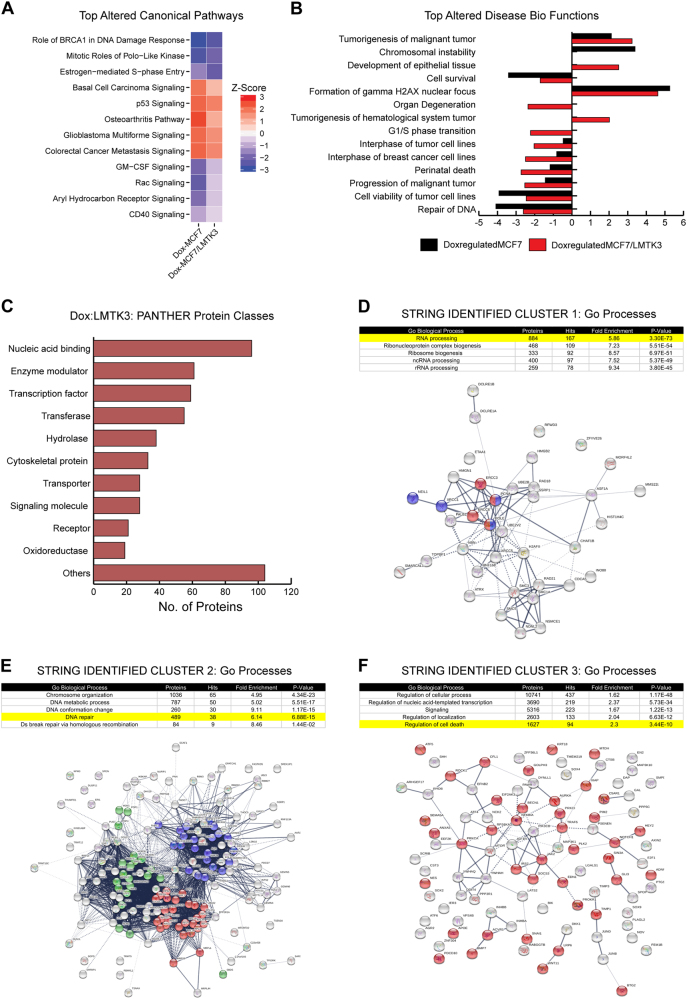
Fig. 5.
Functional analysis of doxorubicin-LMTK3 mediated differential gene expression. a Heatmaps comparing Z scores of canonical pathways significantly enriched for doxorubicin regulated genes identified from doxorubicin/DMSO treated MCF7 and MCF7/LMTK3 cells. The significant P-values were calculated by Fisher’s exact test. The activation or inhibition of the canonical pathways and disease bio functions is given by Z score. A Z score of ≥2 is considered as significant activation and a Z-value of ≤−2 is considered as significant inhibition. The Z score between (0, 2) or (−2, 0) represents trend towards activation or inhibition, respectively. b A bar graph comparing Z scores of disease biological functions enriched for doxorubicin regulated genes identified from doxorubicin/DMSO treated MCF7 and MCF7/LMTK3 cells. c Functional classification of Dox:LMTK3 genes identified using PANTHER classification system. d–f GO pathways analysis of the protein-protein interaction clusters identified in Dox:LMTK3 genes using fast-greedy algorithm provided with STRING database. The STRING network analysis was then performed on gene products involved in RNA processing (d: Cluster 1), DNA repair (e: Cluster 2), and regulation of cell death (f: Cluster 3). The blue, red and green color in STRING network of RNA processing represents proteins involved in splicesome, ribosome and ribosome biogenesis respectively. The red and blue color in STRING network of DNA repair represents proteins involved in Nucleotide Excision Repair and Base Excision Repair. The red color in STRING network of regulation of cell death represents proteins involved in downregulation of apoptotic pathways. For all the STRING networks, the strength of the black line indicates strength of the data support for a given protein-protein association