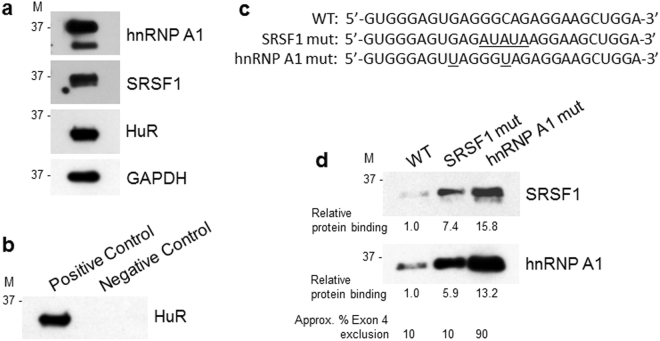
Figure 5.
RNA pull-down analysis of SRSF1 and hnRNP A1 binding to their original and mutated RNA cis-acting motifs identified in exon 4. (a) HEK293T cells express hnRNP A1, SRSF1 and HuR proteins. Whole cell lysates used in RNA pull-down assays were analyzed by western blotting for the expression of endogenous hnRNP A1, SRSF1, HuR and GAPDH. Protein size markers (M) in kDa are indicated. (b) Immunoblotting analysis of HuR protein pulled down from HEK293T cell lysate using biotinylated fragment of the androgen receptor 3′-UTR RNA that contains HuR binding sites (Positive Control) or poly(A)25 RNA with no HuR binding sites (Negative Control). (c) Sequences of 3′-biotinylated RNA probes used for RNA pull-down assays. RNA probes encompass a 27-nucleotide fragment (nucleotides 23 to 49) of exon 4 that contain the putative RNA motifs for binding of SRSF1 and hnRNP A1 proteins (Fig. 3a). WT, a wild-type sequence contains predicted SRSF1 and hnRNP A1 binding sites; SRSF1 mut sequence contains mutations predicted by ESEfinder 3.0 to abolish or, as predicted by HSF 3.0, to reduce SRSF1 binding; hnRNP A1 mut represents RNA probe with hnRNP A1 consensus motif UAGGGU. Introduced mutations are underlined. (d) Immunoblotting analysis of SRSF1 and hnRNP A1 proteins pulled down using a wild-type (WT) and mutated SRSF1 and hnRNP A1 RNA probes described in (c). The biotinylated RNA probes were incubated with 100 μg of HEK293T cell lysate and bound proteins were separated by gel electrophoresis and immunoblotted for SRSF1 and hnRNP A1. The same exposure times for SRSF1 and hnRNP A1 are shown. Protein binding to mutated RNA probes was expressed relative to binding to the WT RNA probe and was calculated from the densitometric intensities of protein bands. Indicated approximate exon 4 exclusions from minigene transcripts are based on results shown in Figs 3 and 4. M, protein size markers in kDa. The gel images (a,b and d) were cropped. The full gel images are shown in Supplementary Fig. 5.