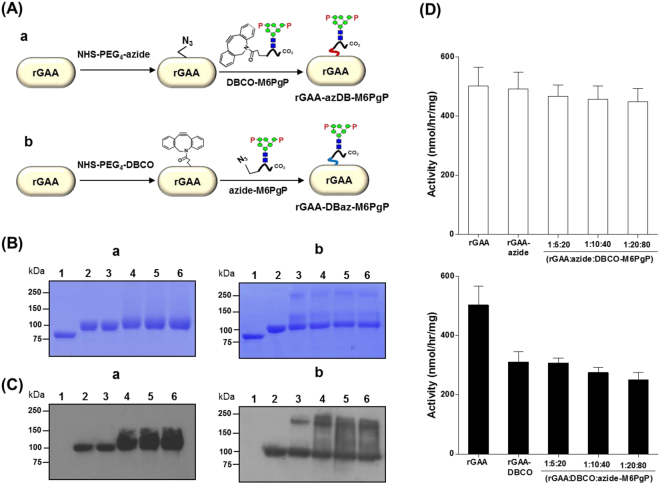
Figure 3.
Conjugation of rGAA with M6PgPs by using copper-free click chemistry. (A) Two different routes to generate M6PgP-conjugated rGAA are schematically represented. In (a) route, rGAA was conjugated with NHS-PEG4-Azide and the resulting rGAA-azide was linked to DBCO-M6PgP made by M6PgP and DBCO-PEG4-NHS conjugation. This reaction product was designated as rGAA-azDB-M6PgP. In (b) route, rGAA was conjugated with DBCO-PEG4-NHS and the resulting rGAA-DBCO was linked to azide-M6PgP, which generated rGAA-DBaz-M6PgP. (B) Sizes of rGAA and its conjugates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE. (C) M6P glycans of rGAA and its conjugates were detected by using Dom9–3xFlag-His8 blotting analysis: lane 1: PNGase F-treated rGAA, lane 2; rGAA, lane 3; rGAA-azide (a) and rGAA-DBCO (b), lane 4–6; 1:5:20, 1:10:40, and 1:20:80 [rGAA:NHS-PEG4-Azide:DBCO-M6PgP (a) and rGAA:NHS-PEG4-DBCO:azide-M6PgP (b)] molar ratio reaction products. (D) Enzyme activities of rGAA-azDB-M6PgP and rGAA-DBaz-M6PgP are represented by white (a) and black (b) bars, respectively. The data represent the averages of three repeated experiments with standard deviations (error bars).