Figure 1.
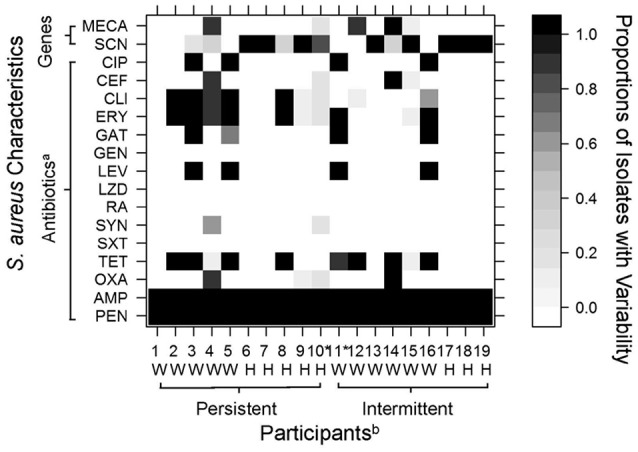
Variability among 10 S. aureus isolates recovered from nasal swabs collected from 19 industrial hog operation (IHO) workers and their household members. Variation in color indicates the observed diversity in tested characteristics, with white cells denoting that no isolates were resistant to a tested antibiotic or positive for a particular gene (i.e., mecA, scn), black cells denoting that all 10 isolates were resistant or positive for a particular gene (i.e., mecA, scn), and gray cells denoting variability among isolates as shown in the legend. aCIP, ciprofloxacin; CEF, ceftriaxone; CLI, clindamycin; ERY, erythromycin; GAT, gatifloxacin; GEN, gentamicin; LEV, levofloxacin; LZD, linezolid; RA, rifampin; SYN, quinupristin/dalfopristin; SXT, sulfamethoxazole with trimethoprim; TET, tetracycline; OXA, oxacillin; AMP, ampicillin; PEN, penicillin. mecA, methicillin resistance gene; scn, scn human immune evasion cluster gene. bW, Industrial Hog Operation (IHO) Worker; H, Household Member. *Participants 10 and 11 carried two different spa types. Other participants each carried a single spa type.
