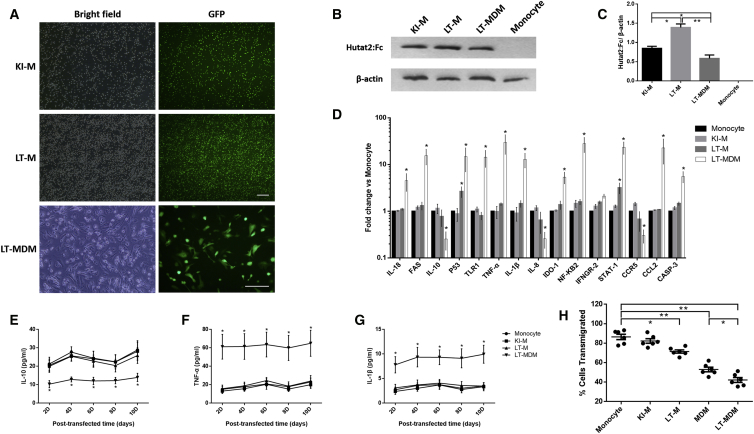
Figure 6.
Evaluation of the Efficiency and Adverse Effects of CRISPR- and Lentivirus-Mediated Transduction of Primary Monocytes or MDMs
(A) The cells were transfected and sorted for suspension monocytes. Representative images of monocytes or MDMs transduced with Hutat2:Fc using different gene-editing methods are shown. Scale bars, 100 μm. (B) Detection of Hutat2:Fc in KI-Ms, LT-Ms, and LT-MDMs by western blotting. Monocyte, non-transfected monocytes. (C) Ratios of the mean values for Hutat2:Fc to β-actin in each cell type shown in (B) (n = 5). One-way ANOVA was employed for the statistical analyses. (D) Comparison of the levels of 15 monocyte-related regulatory genes in each group by real-time PCR (n = 6). (E–G) Comparison of the IL-10 (E), TNF-α (Φ), and IL-1β (G) levels in the culture supernatants of each group by ELISAs (n = 5). (H) Comparison of the cellular transmigration rates of each group using TEM assays (n = 6). Dunnett’s t tests were used for the statistical analyses of the data shown in (D)–(H); *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. The results are presented as the means from independent experiments. The error bars denote the SEM. KI-M, CRISPR/Cas9-mediated Hutat2:Fc KI monocytes; LT-M, lentivirus-transfected monocytes; LT-MDM, lentivirus-transfected monocyte-derived macrophages.