Figure 5.
Interaction of BKV with GT1b and Heparin
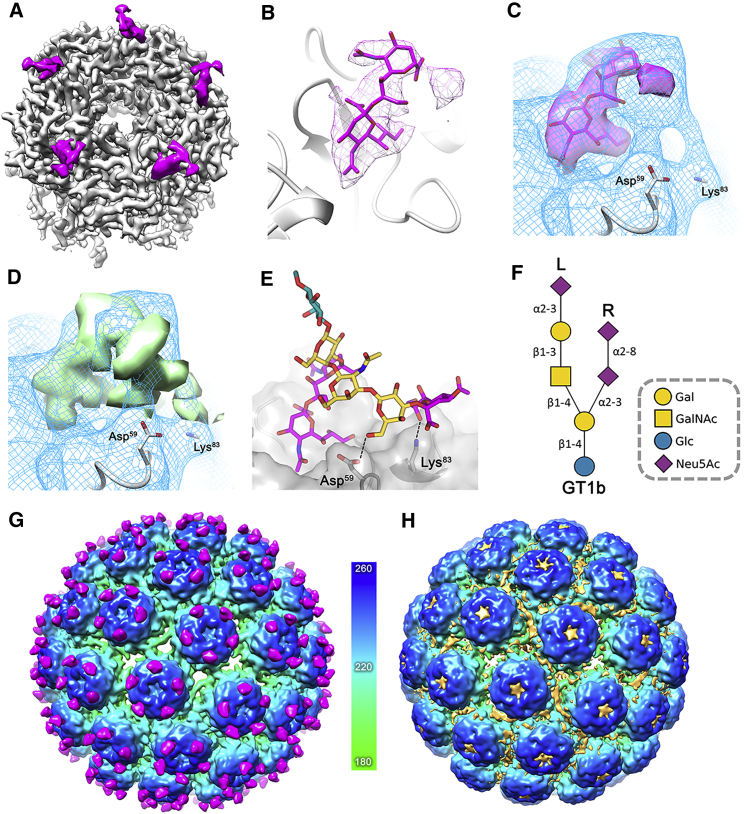
(A) Isosurface representation of a single 5-fold pentamer of the BKV-GT1b complex with the capsid colored as in Figure 2 and GT1b (magenta).
(B) Enlarged view of the GT1b density (2 σ) containing the corresponding atomic model for the disialic acid motif of the right arm, colored as in (D).
(C) The 5 Å low-pass-filtered BKV-GT1b EM density (blue mesh) containing the high-resolution information shown in (B).
(D) MD-derived atom density map for the simulated structure of GT1b overlaid with the 5 Å low-pass-filtered EM density shown in (C).
(E) A snapshot of the MD simulated structure of GT1b showing possible interactions of the left arm with Asp59 and Lys83.
(F) SNFG-representation of GT1b oligosaccharide showing the left and right arms of the molecule (Varki et al., 2015).
(G) Isosurface representation of the unsharpened and 8 Å low-pass-filtered BKV-GT1b map viewed down the icosahedral 2-fold axis and colored according to the radial coloring scheme shown (Å). The GT1b difference density (3.4 σ) is shown colored magenta.
(H) The unsharpened and 8 Å low-pass-filtered isosurface representation of the BKV-heparin structure, with the putative heparin difference density (3.4 σ) colored orange.