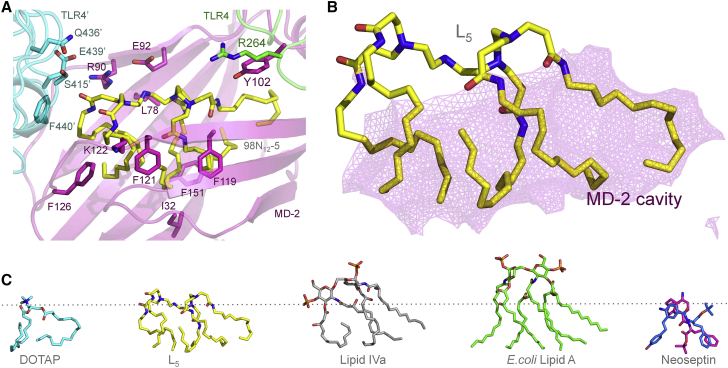
Figure 2.
Binding Mode of L5
(A) Graphical representation of L5 (yellow) binding to TLR4/MD-2 with primary TLR4 (green), secondary TLR4 at the dimer interface denoted TLR4’ (cyan), and MD-2 (magenta). L5 and its closest protein contacts are shown as sticks with oxygen (red) and nitrogen (blue) atoms. (B) Close-up of L5 filling up the hydrophobic cavity of MD-2 is shown: the solvent-accessible pocket of MD-2 is represented as a semi-transparent pink mesh. (C) Different ligand conformations predicted for TLR4/MD-2 binding are shown: DOTAP, L5, and the species-specific antagonist lipid IVa as observed in complex with human MD-2 (PDB: 2E59); the potent agonist E. coli lipid A (PDB: 3FXI); and the species-specific agonist neoseptin, as observed in complex with mouse TLR4/MD-2 (PDB: 5HG4). The dotted line represents the same position of the ligand in the MD-2 cavity (see also Figure S3).