Figure 1.
Titer and Transfer Efficiency of IDLVs Packaged with Integrase-Fused hyPBase
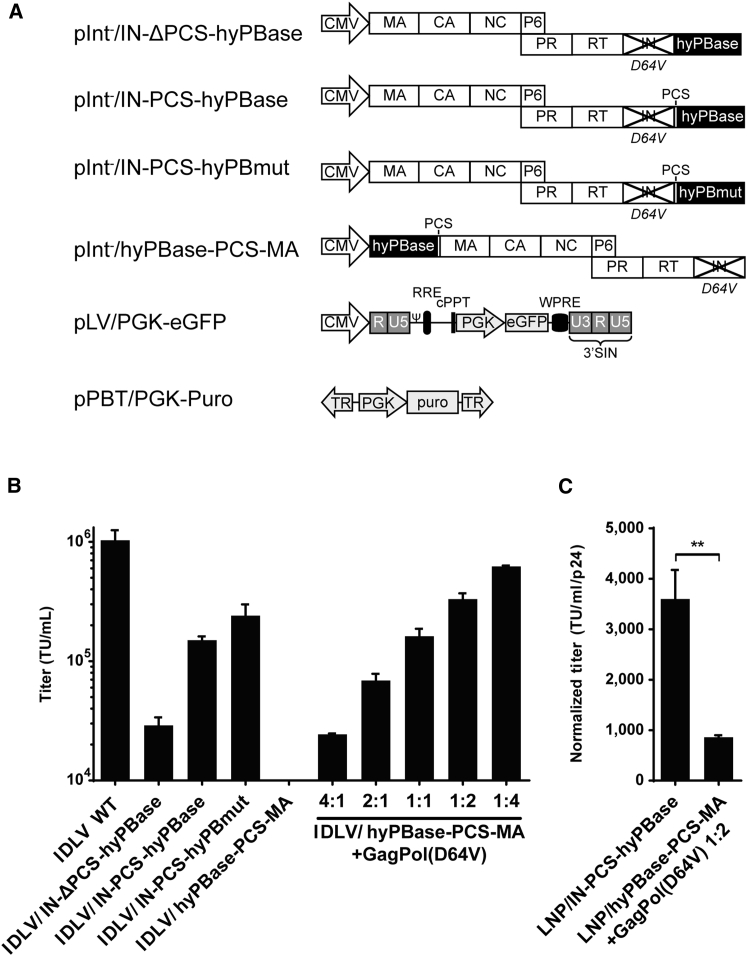
(A) Schematic representation of the constructs used in the study. (B) Evaluation of transduction titers of transposase-loaded IDLVs carrying vector RNA encoded by pLV/PGK-EGFP is shown. IDLVs with IN-fused PB transposase with or without the KARVL/AEAMS protease cleavage site (PCS) were packaged with a PGK-EGFP expression vector, and transduction titers were estimated by flow cytometry and compared to IDLVs packaged with MA-fused transposase in the presence of increasing amounts of wild-type Gag/GagPol (GagPol-D64V), as indicated by the ratios. A standard IDLV was furthermore included as a control. (C) Estimation of IDLV transfer efficiency is shown. The total amount of LNPs was estimated by p24 ELISA and used to normalize transduction titers quantified in (B) to estimate the relative transfer efficiency of IDLVs packaged with IN- or MA-fused PB transposase. cPPT, central polypurine tract; CA, capsid; IN, integrase; MA, matrix; NC, nucleocapsid; PR, protease; RT, reverse transcriptase; Ψ, psi packaging signal; RRE, rev response element; WPRE, woodchuck hepatitis virus post-transcriptional regulatory element. Data are presented as mean ± SEM and n ≥ 3.