Figure 6.
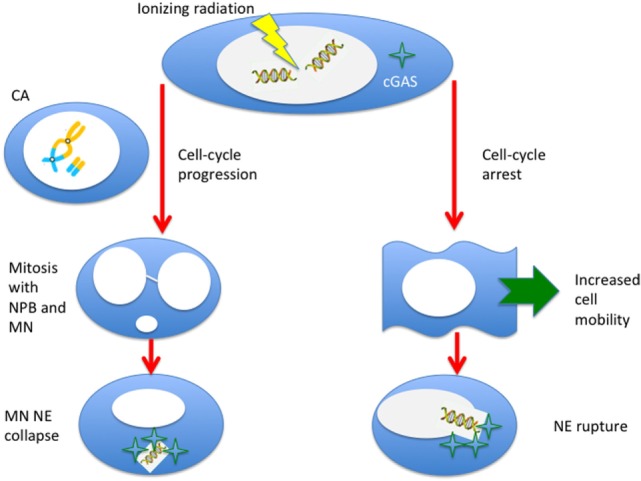
Ionizing radiation can induce cytosolic DNA, thus triggering the cyclic GMP–AMP synthase (cGAS)/stimulator of interferon genes (STING) pathway, in two different ways. If cells progress to mitosis carrying chromosome aberrations, MN (from acentric fragments) can be produced at the first mitosis along with nucleoplasmic bridges (NPB, from dicentrics). These micronuclei can be incorporated in the cytoplasm of the daughter cells and, following the collapse of the nuclear envelope (NE), can be sensed by the cGAS. Alternatively, even if the cell is blocked or delayed in the cell-cycle, radiation-induced DNA fragments can leak through a damaged NE. This effect can be more likely for very small fragments induced by densely ionizing radiation, and NE rupture can be triggered by the enhanced mobility of the cells following radiation exposure.
