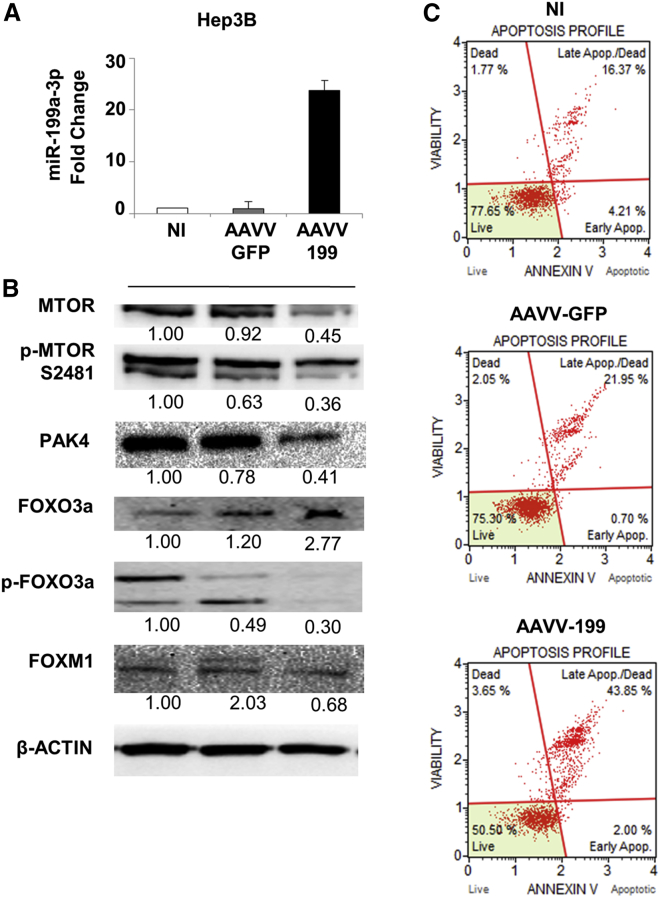
Figure 5.
Overexpression of miR-199a-3p Increased Apoptosis Levels in Hep3B Cells by Affecting MTOR and PAK4 Pathways
miR-199a-3p expression increased in Hep3B cells by an adeno-associated viral vector (AAVV) expressing miR-199a-3p (AAVV-199). As experimental controls, the cells were infected with a control virus AAVV- GFP or uninfected. Cells were collected and analyzed 120 hr after infection. (A) The expression levels of miR-199a-3p in the infected cells were determined by qPCR, and proteins were analyzed using immunoblot. miR-199a-3p levels were significantly higher in cells infected with AAVV-199 compared to the controls (p < 0.0001). All the data reported are an average of the experiment performed in triplicate (mean + SD). (B) The increased expression of miR-199a-3p-related genes involved in the MTOR and PAK4 pathways. In samples infected with AAVV-199, immunoblotting analyses revealed a downregulation of MTOR and its phosphorylated form p-2481, PAK4, the phosphorylated form of forkhead box O3 (FOXO3a), and FOXM1 compared to the controls (AAVV-GFP, NI). (C) Cells treated with miR-199a-3p showed a considerable increase in the percentage of total apoptosis compared to control cells. Notably, the control virus AAVV-GFP did not induce appreciable changes in cell viability (live cells in the plot) compared to the uninfected control, indicating the non-toxicity of the virus itself and the specificity of the effect mediated by AAVV-199.