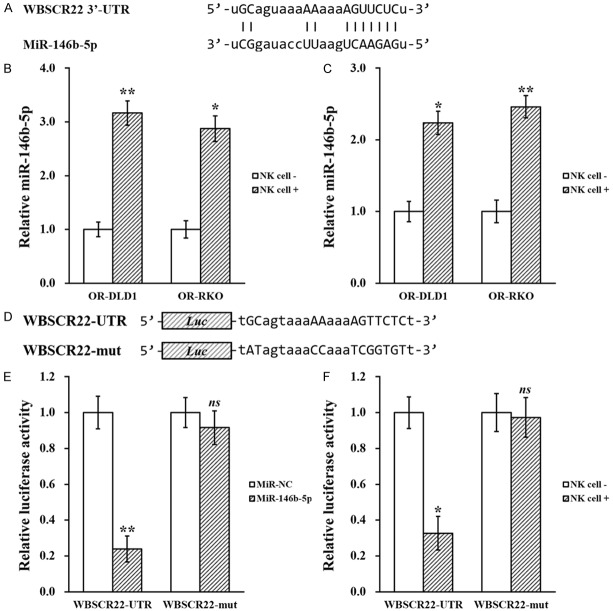
Figure 6.
MiR-146b-5p directly targets WBSCR22 mRNA 3’-UTR to inhibit its expression. A. Predicted miR-146b-5p targeting sequence on the 3’-UTR of WBSCR22 mRNA. B. Oxaliplatin-resistant (OR)-DLD1 and OR-RKO cells in the absence (NK cell -) or presence (NK cell +) of co-cultured natural killer cells, respectively, were subjected to microRNA assay to assess miR-146b-5p levels. C. At the end of day 21, OR-DLD1 and OR-RKO xenograft tumors from all mice were extracted and subjected to microRNA assay to assess miR-146b-5p levels. D. Wild type (WBSCR22-UTR) targeting sequence of miR-146b-5p on 3’-UTR of WBSCR22 mRNA, and the mutated version (WBSCR22-mut), were cloned at the downstream of the luciferase open reading frame (Luc). E. Luciferase activities of WBSCR22-UTR or WBSCR22-mut constructs were examined after stable expression of miR-NC or miR-146b-5p, respectively. F. Luciferase activities of WBSCR22-UTR or WBSCR22-mut constructs were examined in the absence (NK cell -) or presence (NK cell +) of co-cultured natural killer cells, respectively. Data are presented as mean ± SD, from at least three independent in vitro experiments, or n=8 each group for animal experiments. **P<0.01, *P<0.05, ns not significant, NK cell - vs NK cell +, or miR-NC vs miR-146b-5p.