Figure 1.
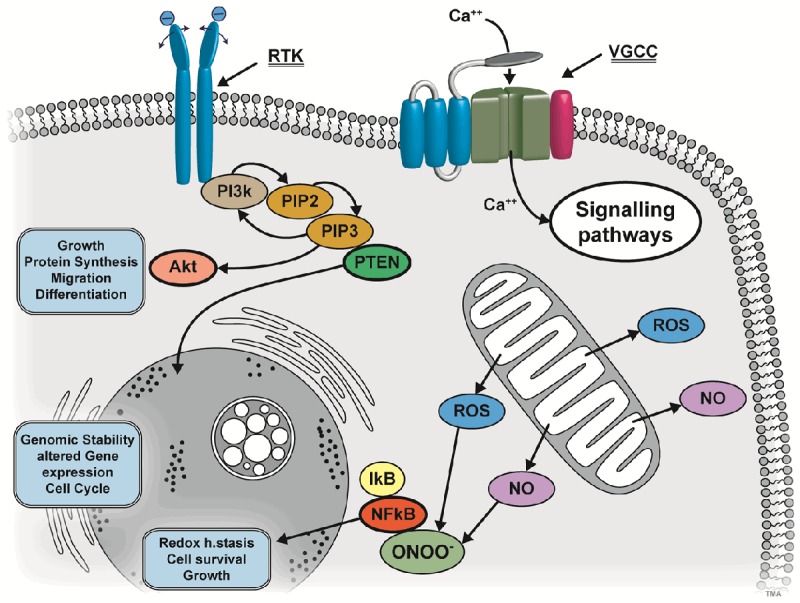
Different ways of PEMF-coupling to molecular biology of the cell: Upper left: ligands with polar moieties can go into resonance with PEMF-frequencies. Downstream events are elicited e.g. via receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK) PIP2 (Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-biphosphate), PIP3 (Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate) and lipid Phosphatase PTEN (Phosphatase and Tensin homolog). PIP3 can signal further via Akt and Akt itself is the center of many other signaling pathways. Thus, many functional ways can be accessed by these signaling cascades. Upper right: voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs) can be addressed directly by PEMF. The Ca++ stream into the cell can act on many other pathways and organelles. Bottom right: PEMF can also act by its magnetic component on radical production and in medium with oxygen also to radical oxygen species (ROS). Further, by spin triplet reorientation also a directional component can be induced. Nitric oxygen (NO) can also be released from mitochondria by PEMF and by radical production. NO and ROS in turn can also react to peroxynitride (ONOO-). This in turn will activate IκB and NFκB and this can elicit in “moderate” amounts cell reactions which lead to a kind of “pre-conditioning” and protection.
