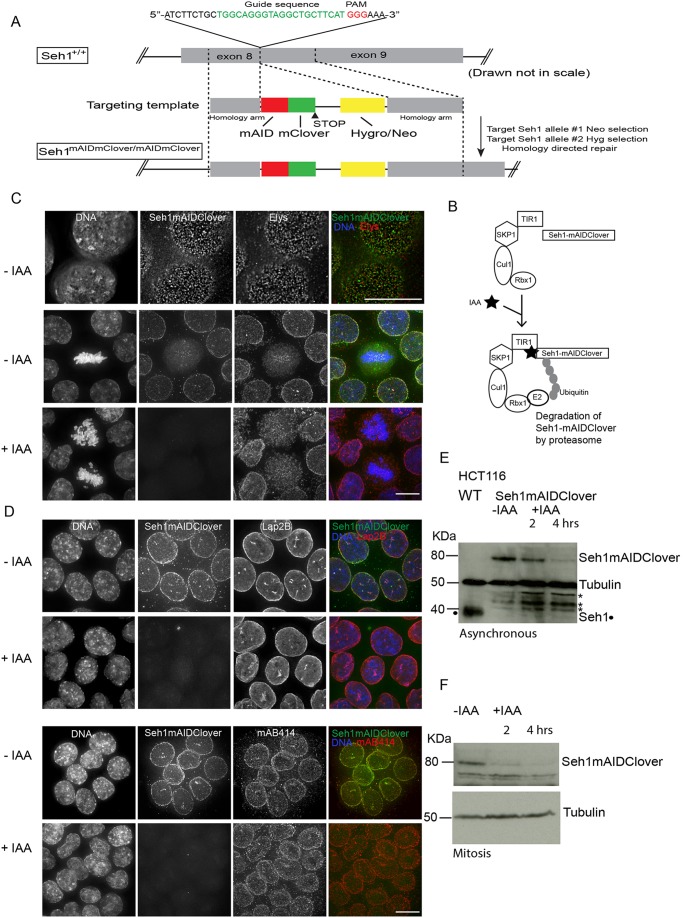
Fig. 1.
Establishment of a rapid auxin-inducible Seh1 degradation system. Establishment of Seh1–mAIDmC HCT116 cells expressing OsTIR1 and Seh1–mAID–mClover. (A) Strategy for the insertion of the mAID–mClover coding sequence just upstream of the termination codon of the human Seh1 gene. A schematic diagram of the guide (g)RNA/targeting template-targeting site at Seh1 exon 8 is shown. The gRNA sequence is shown in green and PAM motif in red. The targeting template contains 500 bp homology arms that flank the double-strand break site and a mAID–mClover Hygro or/Neo cassette. The genomic configuration expected to be generated via homology-directed repair is shown underneath. (B) Schematic illustration of the AID system. OsTIR1 is part of the SCFOsTIR1 E3 ligase complex, and works together with an endogenous E2. Upon addition of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), Seh1 protein tagged with mAID is polyubiquitylated and degraded. (C,D) The subcellular localisation of Seh1–mAID–mClover (green) is shown in interphase or mitotic cells in the absence or presence of IAA (4 h). Cells were counterstained for the Nup107 complex member (Elys, red), a nuclear envelope component (Lap2B) (red), and FG repeat nucleoporins (mAB414) (red). DNA is shown in blue. (E) Immunoblots of total cell lysates of from the HCT116 OsTIR1 parental cell line and Seh1-mAIDmC cell line in the absence (−IAA) or presence (+IAA) of auxin during interphase (E) or mitosis (F) probed using anti-Seh1 and anti-tubulin. Seh1–mAIDmC cells were synchronised in mitosis with Monastrol and were either mock treated or treated with IAA for the corresponding amount of time still in the presence of Monastrol. Tubulin serves as a loading control. *non-specific band (Seh1 is marked with a black dot). Scale bars: 10 µm.