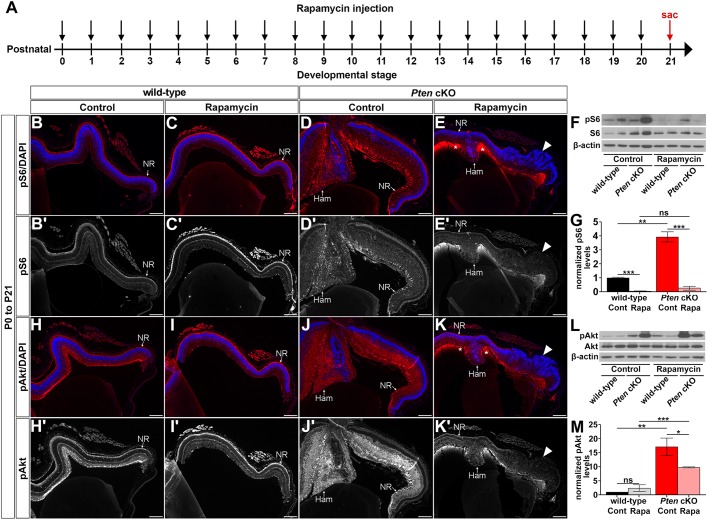
Fig. 7.
Rapamycin treatment beginning at P0, prior to the onset of hamartoma formation, worsens defects in the retinal architecture in Pten cKO retinas. (A) Schematic of experimental timeline. Black arrows indicate rapamycin administration, and red arrow indicates the time point when mice were collected (sac, sacrifice at P21). (B-E′) P21 wild-type and Pten cKO retinas collected from animals administered vehicle alone (B,B′,D,D′) or rapamycin (C,C′,E,E′) for 21 days (from P0) and immunolabelled with pS6Ser235/236 (wild-type control: n=7, Pten cKO control: n=5, wild-type rapamycin: n=8, Pten cKO rapamycin: n=5). (F,G) Western blot (F) and densitometry (G) of pS6Ser235/236 labelling of P21 wild-type and Pten cKO retinal lysates treated with vehicle alone or rapamycin (wild-type control: n=9, Pten cKO control: n=9, wild-type rapamycin: n=9, Pten cKO rapamycin: n=9). (H-K′) P21 wild-type and Pten cKO retinas collected from animals administered vehicle alone (H,H′,J,J′) or rapamycin (I,I′,K,K′) for 21 days (from P0) and immunolabelled with pAktSer473 (wild-type control: n=7, Pten cKO control: n=5, wild-type rapamycin: n=8, Pten cKO rapamycin: n=5). (L,M) Western blot (L) and densitometry (M) of pAktSer473 labelling of P21 wild-type and Pten cKO retinal lysates treated with vehicle alone or rapamycin (wild-type control: n=9, Pten cKO control: n=9 from three litters; wild-type rapamycin: n=9, Pten cKO rapamycin: n=9). Blue is a DAPI counterstain. Arrowheads mark the dysmorphic regions of the retina in Pten cKOs treated with rapamycin (E,E′,K,K′). Ham, hamartoma; NR, neural retina. Scale bars: 200 μm. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001.