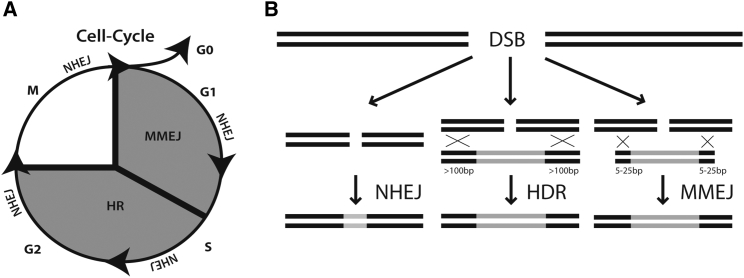
Figure 1.
Double-Strand Break Repair Events
(A) Scheme showing the three preferred repair mechanisms during the cell cycle after DNA double-strand break. The error-prone NHEJ is active during the whole cell cycle. HDR leads to correct repair in late S/G2 phases. The MMEJ repair is active in early M and S phases, and can be used for targeted insertions with small homolog sequences. (B) Scheme of the different repair events highlighting the importance and length of the homologous sequences on the donor template DNA. For HDR, homologous regions of more than 100 bp up to several kbp are needed to edit a given sequence, depending on the size of the sequence to be replaced. For MMEJ, the length of the homologous sequences is about 5–25 bp.