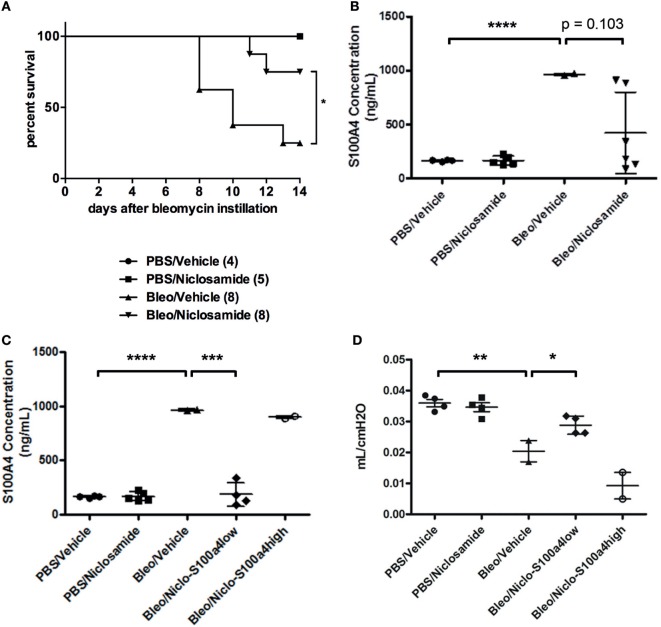
Figure 7.
Niclosamide treatment in vivo. (A) Treatment with niclosamide improves survival of bleomycin-instilled mice. Mice were intratracheally treated with bleomycin, or as a control, with PBS. Beginning at day 7 after bleomycin instillation, mice were treated once daily with niclosamide (20 mg/kg) or vehicle. Mice were monitored daily for signs of disease, and any mice that appeared moribund were sacrificed. Treatment with niclosamide significantly improved the survival of bleomycin-instilled mice [*p = 0.031; Log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test]. Numbers in brackets indicate the total number of mice per group. (B,C) Treatment with niclosamide reduces S100a4 protein in the BAL fluid. The surviving mice depicted in panel (A) were subjected to BAL. The protein concentration of S100a4 in the BAL fluids was determined by ELISA. Each symbol represents a mouse. Results are shown as mean ± SD. Unpaired t-test was performed for statistical analysis (***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001). (D) Treatment with niclosamide improves lung function. The surviving mice depicted in panel (A) were subjected to a lung function test, and lung compliance was determined. Each symbol represents a mouse. Results are shown as mean ± SD. Unpaired t-test was performed for statistical analysis (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01).