Figure 2.
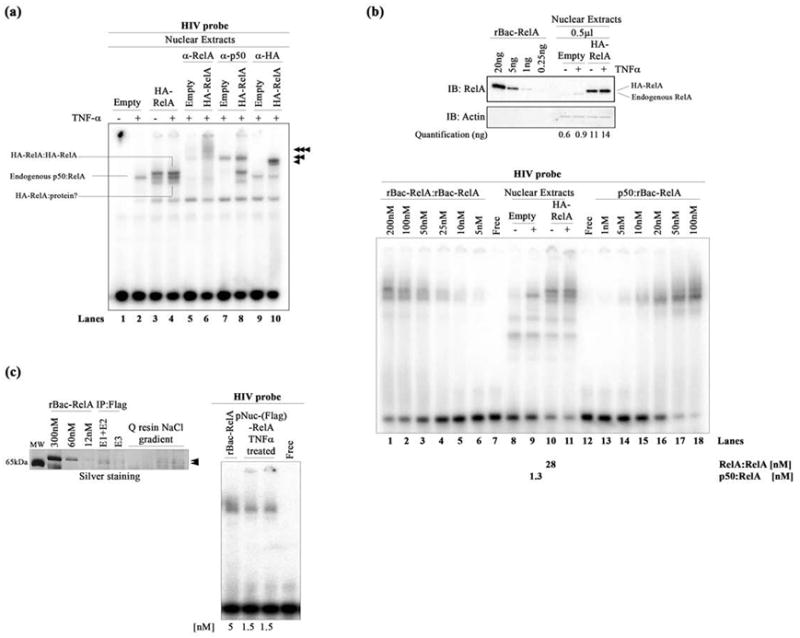
DNA binding by nuclear NF-κB dimers. (a) EMSA showing HIV-κB DNA binding by the exogenous HA-RelA homodimer (top band), endogenous p50:RelA heterodimer (middle band), and additional HA-RelA:protein complex (bottom band) present in transfected HA-RelA nuclear extracts unstimulated or stimulated with TNF-α. Single, double, and triple arrowheads indicate the supershifted complexes when using anti-RelA, anti-p50, and anti-HA antibodies, respectively. (b) The top panel shows a Western blot showing the quantitation of endogenous and exogenous HA-RelA in transfected nuclear extracts. rBac-RelA was used as a standard to perform this estimation. Bands were subjected to densitometry using ImageJ software. Actin was used as the loading control for this experiment. The bottom panel shows an EMSA showing the comparative DNA binding activities of the recombinant rBac-RelA homodimer and p50:rBac-RelA heterodimer and also the homo- and heterodimers present in transfected HA-RelA nuclear extracts. A titration of the recombinant proteins was used to estimate the concentration of NF-κB dimers present in the nucleus. Quantitations obtained are shown at the bottom of the figure. (c) The left panel shows an SDS–PAGE gel stained with silver to estimate the amount of protein present in the pNuc(Flag)-RelA sample. rBac-RelA was used as a standard. Samples that were analyzed show all the steps of the purification of the Flag-RelA protein present in the nuclear fraction. E1–E2 and E3 are the samples obtained after eluting the proteins from the anti-Flag M2 affinity resin. Then, the sample was bound to Q-Sepharose resin and eluted after performing a NaCl gradient. Arrows indicate the pNuc(Flag)-RelA after purification. The right panel shows an EMSA showing the equivalent binding between rBac-RelA and pNuc(Flag)-RelA when using similar amounts of protein (5 and 1.5 nM, respectively).
