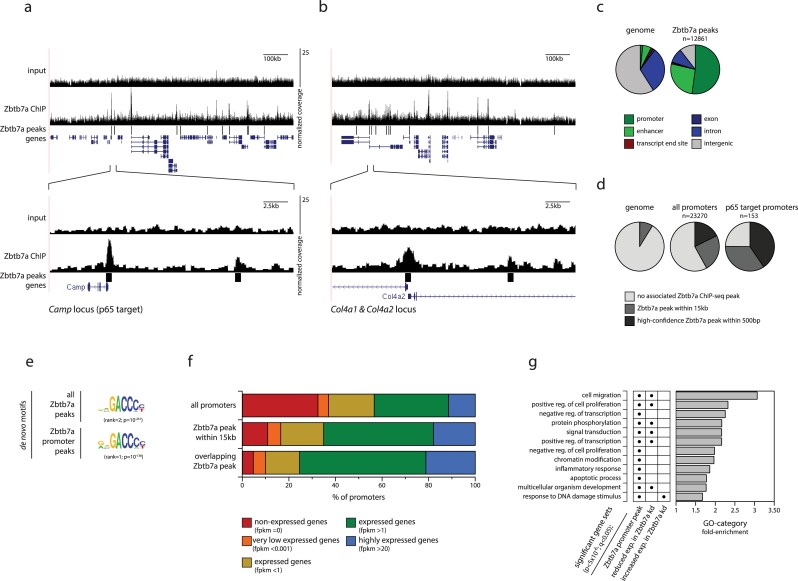
Fig 2. Zbtb7a is a widespread promoter- and enhancer-associated factor.
(A, B) Genome browser example tracks of a Zbtb7a ChIP-seq and input coverage (top) across representative 1 Mb genomic intervals, illustrating the prominent overlap between Zbtb7a peaks and TSSs, and (bottom) zoomed-in on 25 kb regions including the Zbtb7a-bound Camp (A) and Col4a1/2 (B) gene promoters. Lower tracks indicate predicted Zbtb7a binding peaks and RefSeq genes. (C) Fractions of the genome (left pie) and of Zbtb7a ChIP-seq peaks (right pie) that overlap with selected genomic features. (D) Fractions of the genome, of all promoters, and of p65 target promoters that are associated with predicted Zbtb7a ChIP-seq peaks. (E) DNA sequence motifs matching the described binding specificity of Zbtb7a, enriched among all (top) and promoter-associated (bottom) Zbtb7a ChIP-seq peaks, identified by de novo motif prediction. (F) Fractions of all promoters (top) or of promoters overlapping (bottom) or within 15 kb of (middle) predicted Zbtb7a ChIP-seq peaks that are expressed in fibroblasts at the indicated mRNA levels. (G) Enrichment of GO annotations among genes whose promoters are associated with Zbtb7a peaks (first column, “Zbtb7a promoter peak”) or with increased or decreased mRNA expression in control fibroblasts, compared to Zbtb7a-knockdown fibroblasts (second and third columns). Dots indicate statistically enriched annotations (P < 5 × 10−6; corrected q < 0.05). The most-significantly enriched annotations among genes with Zbtb7a-associated promoters are shown, of which some are also enriched among genes exhibiting Zbtb7a-regulated expression. Bars indicate levels of enrichment compared to all annotated genes. Statistical analysis is provided as Supporting information, and numerical values underlying figures are reported in S1 Data. ChIP-seq, chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing; FPKM, RNA-sequencing fragments per kilobase transcript per million reads; GO, gene ontology; RefSeq, NCBI reference sequence database; TSS, transcription start site.