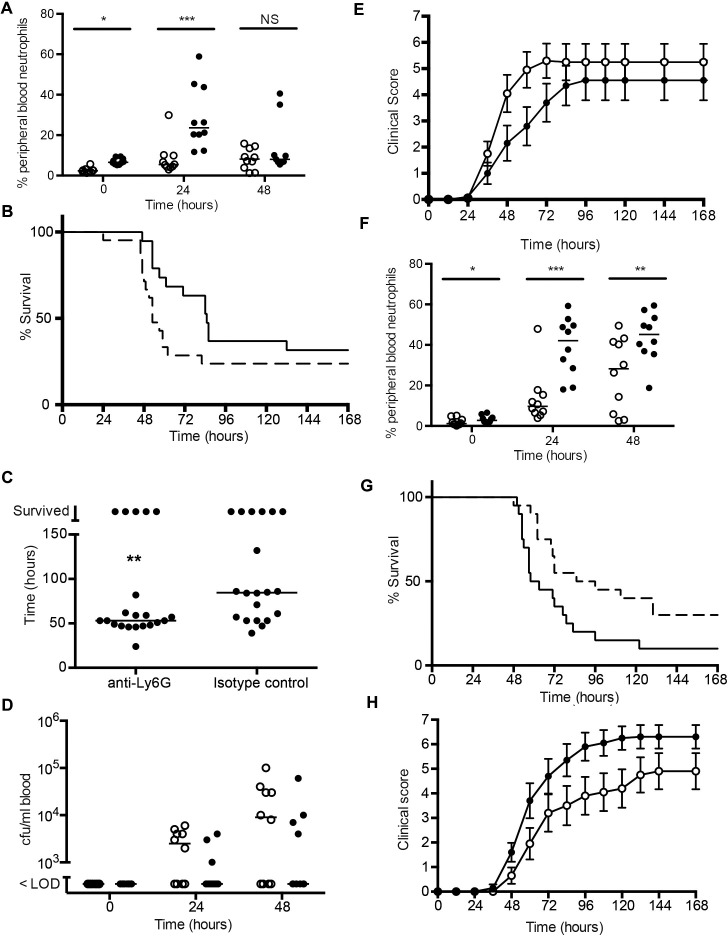
Fig 6. Infection with TIGR4 or SRL1 following depletion of neutrophils.
C57Bl/6 mice (20 per group) were infected with 106 cfu/mouse of TIGR4 (A-D) or SRL1 (E-F) by intranasal inoculation 24 hours after intraperitoneal inoculation of 500 μg antibody 1A8 (anti-Ly6G) or isotype matched control and observed for the course of the infection. (A) peripheral blood neutrophil counts following treatment with isotype control (filled circles) or anti-Ly6G (open circles) at indicated times following infection. Differences (Mann Whitney test) were not significant (NS) or significant (*, p < 0.05, ***, p < 0.001) (B) Isotype control treated mice (solid line) and neutrophil depleted mice (dashed line) had similar survival (A, P = 0.09, log rank test). (C) Median survival time among neutrophil depleted mice; each point is an individual animal, line is median. Differences are significant (**, Mann Whitney test, p = 0.01). (D) bacteremia and (E) clinical score between isotype treated mice (solid circles) and neutrophil depleted mice (open circles). Differences are not significant. (F) as (A) following infection with SRL1 (G) Outcome following SRL1 infection. Isotype control treated mice (solid line) had impaired survival compared to neutrophil depleted mice (dashed line) (p = 0.02, log rank test). (H) Clinical score in neutrophil depleted mice (open circles) compared to isotype treated mice (solid circles). Differences between the groups are significant (p = 0.01, 2-way ANOVA corrected for repeated measures).