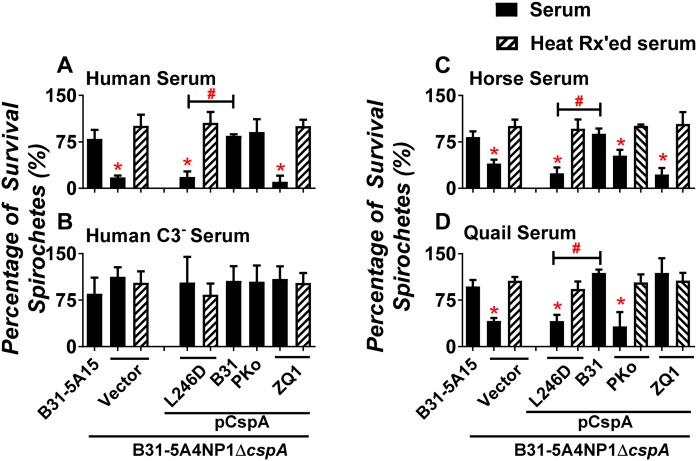
Fig 4. CspA variants mediate distinct levels of spirochete survival in serum from different vertebrate animals.
B. burgdorferi strain B31-5A15 (“B31-5A15”), B31-5A4NP1ΔcspA harboring the vector pBSV2G (“ΔcspA/Vector”), or this cspA mutant strain producing CspAB31 (“ΔcspA/pCspAB31”), CspAPKo (“ΔcspA/pCspAPKo”), CspAZQ1 (“ΔcspA/pCspAZQ1”), or CspAB31L246D (“ΔcspA/pCspAB31L246D”) was incubated for four hours with untreated (filled bars) or heat-inactivated (HI, hatched bars) serum with a final concentration of 40%. These sera include (A) human serum or (B) C3-depleted human serum (Human C3- serum) or the serum from (C) horse or (D) quail. The number of motile spirochete was assessed microscopically. The percentage of survival for those B. burgdorferi strains was calculated using the number of mobile spirochetes at four hours post incubation normalized to that prior to the incubation with serum. Each bar represents the mean of three independent determinations ± SEM. Significant differences (P < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni correction) in the percentage survival of spirochetes relative to the ΔcspA/Vector (“*”) or between two strains relative to each other (“#”).