Figure 7.
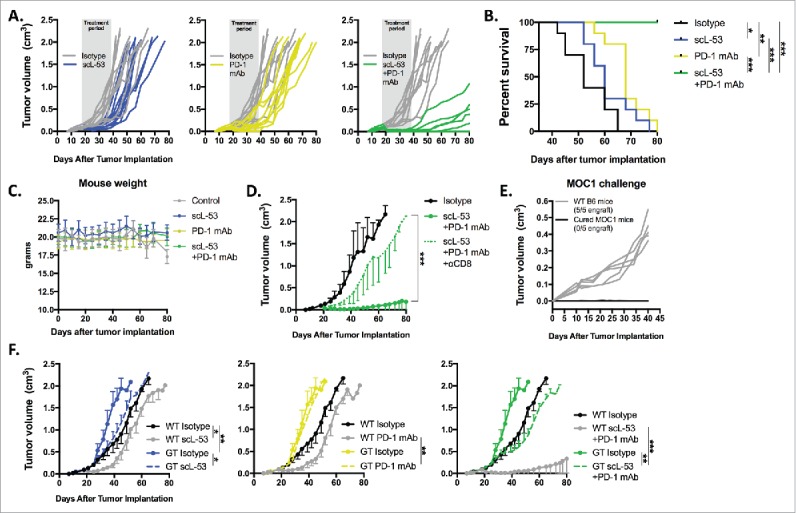
Combination scL-53 and PD-1 mAb induces CD8 and host STING-dependent rejection of a subset of established MOC1 tumors. Individual growth curves (A) and survival (B) following treatment of established MOC1 tumors (n = 9–10 mice/condition) with scL-53 (30 μg/injection, twice weekly x 3 weeks) alone or in combination with PD-1 mAb (200 μg twice weekly 3 weeks). C, treated MOC1 tumor-bearing mouse weight was plotted over time. D, treatment with combination scL-53 plus PD-1 mAb as in A was repeated with or without CD8+ cell depletion (clone YTS 169.4, n = 5 mice/condition)). E, naïve WT B6 mice or WT B6 mice that rejected established MOC1 tumors after combination scL-53 and PD-1 mAb treatment were challenged with subcutaneous injection of 3 × 106 MOC1 cells and followed for tumor engraftment. F, MOC1 tumors were established in STING-deficient mice (GT; Tmem173gt, n = 5 mice/condition) and scL-53 treatment was repeated with or without PD-1 mAb as in A. Summary growth curves were analyzed via ANOVA of tumor volume at day 40 after tumor engraftment. For all in vivo experiments, shown are representative results from one of two independent experiments. Control mice for these experiments received TVI of PBS and IP injection of 200 μg of rat IgG2 Ab twice weekly. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, P,0.001.
