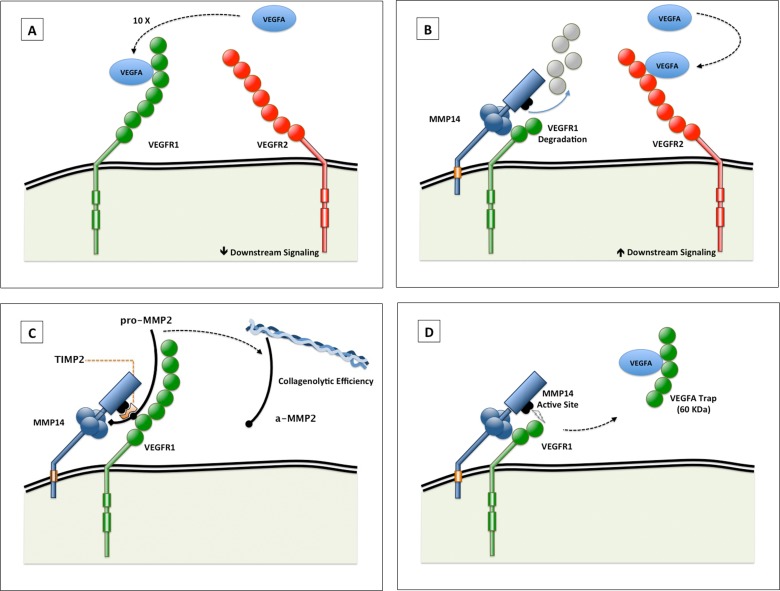
Figure 1.
(A, B) Schematic illustration of the proangiogenic role of VEGFR1 binding to, and selective degradation by, MMP14. Vascular endothelial growth factor A has greater binding affinity for VEGFR1 than VEGFR2 (A). Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 binding to, and degradation by, MMP14 increases the availability of VEGFA to VEGFR2, which increases downstream signaling (B). Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 and VEGFR2 dimers are depicted as monomers in this figure for illustrative purposes. (C, D) Schematic illustration of possible alternative proangiogenic roles of VEGFR1–MMP14 interactions. (C) VEGFR1 interaction with MMP14 altering the activation of pro-MMP2, in the presence of an optimal TIMP2 concentration. The activated MMP2 serves to increase the collagenolytic efficiency of MMP14. (D) Matrix metalloproteinase 14 cleavage of VEGFR1 can free a 60-kDa fragment that may trap VEGFA. The affinity of VEGFA to this fragment is less than its affinity to intact VEGFR1 but more than its affinity to VEGFR2.28