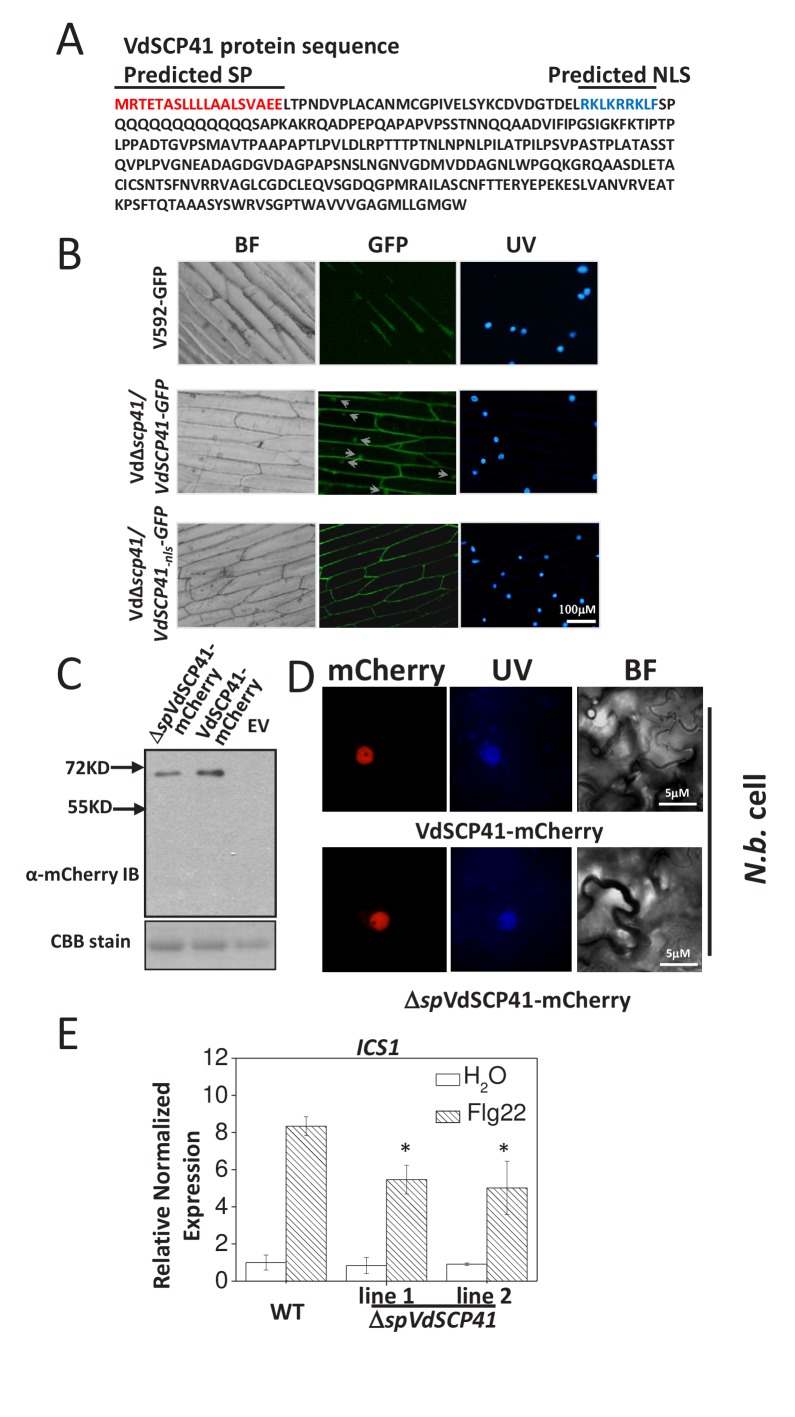
Figure 2. VdSCP41 functions to inhibit immunity in plants.
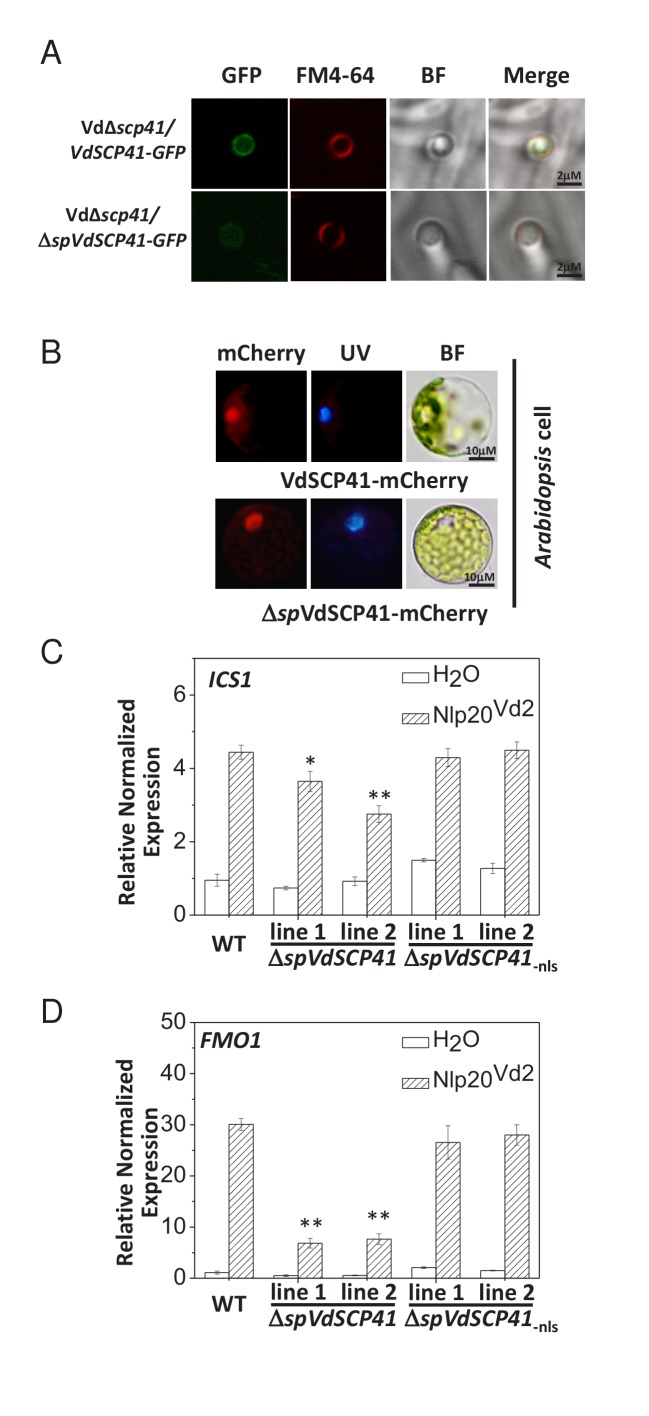
(A) VdSCP41 localizes to the base of the hyphopodia and forms ring signals surrounding the hyphal neck. The Vd∆scp41/VdSCP41-GFP strain and Vd∆scp41/ΔspVdSCP41-GFP was cultured on a cellophane membrane for 5 days to induce the formation of hyphopodia. Localization of VdSCP41-GFP was visualized using a Leica SP8 microscope. (B) Transiently expressed VdSCP41 preferentially localizes to the nucleus of Arabidopsis cells. Arabidopsis protoplasts were transfected with either a VdSCP41-mCherry or a ΔspVdSCP41-mCherry plasmid as indicated. mCherry fluorescence was visualized 16 hr post transfection. DAPI staining of the nucleus was visualized under UV light. (C–D) Expression of ΔspVdSCP41 in Arabidopsis inhibits nlp20Vd2-induced ICS1 (C) and FMO1 (D) expression. Wildtype (WT) and transgenic plants expressing ΔspVdSCP41 or ΔspVdSCP41-nls were treated with H2O or nlp20Vd2 as indicated. RNA was extracted for real-time PCR analyses. The experiments were repeated three times with similar results. Error bars indicate standard deviations. Student’s t-test was carried out to determine the significance of difference. * Indicates significant difference at a P-value of < 0.05, whereas ** indicates significant difference at a P-value of < 0.01.
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. VdSCP41 delivered by V. dahliae translocates into plant cells and inhibits immunity.
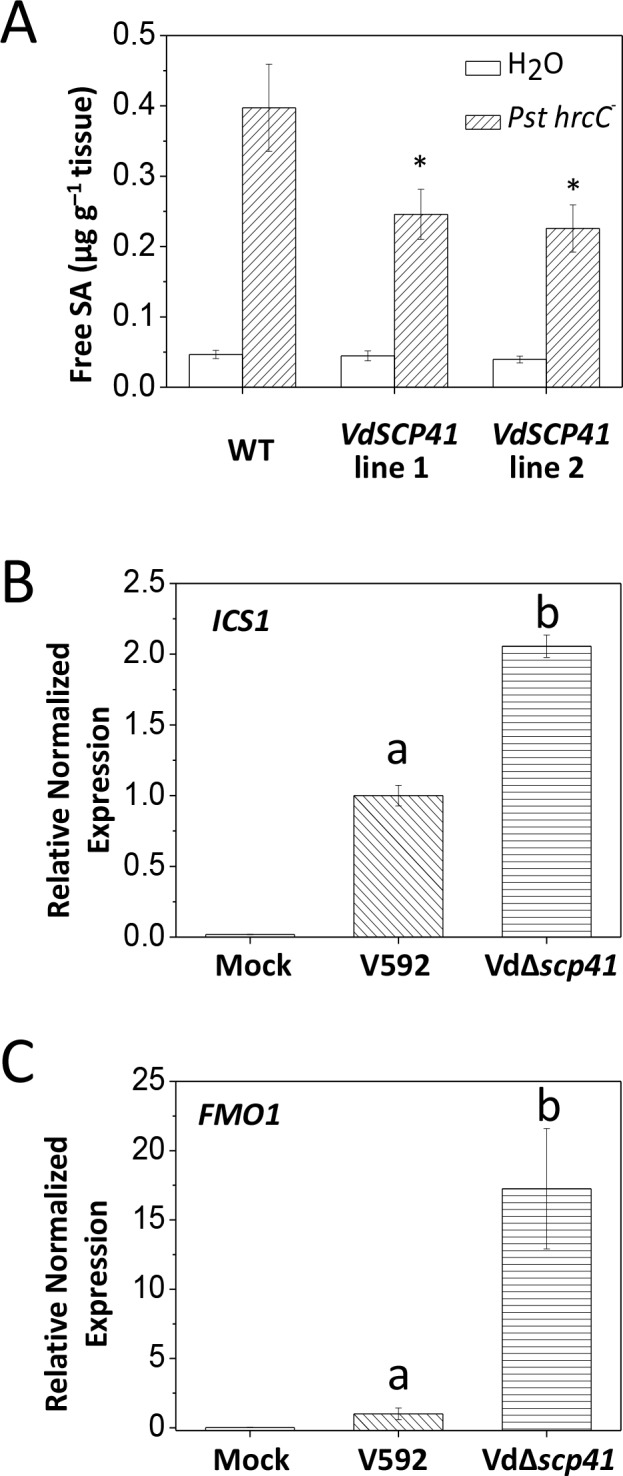
Figure 2—figure supplement 2. VdSCP41 inhibits pathogen-induced SA accumulation and gene expression.