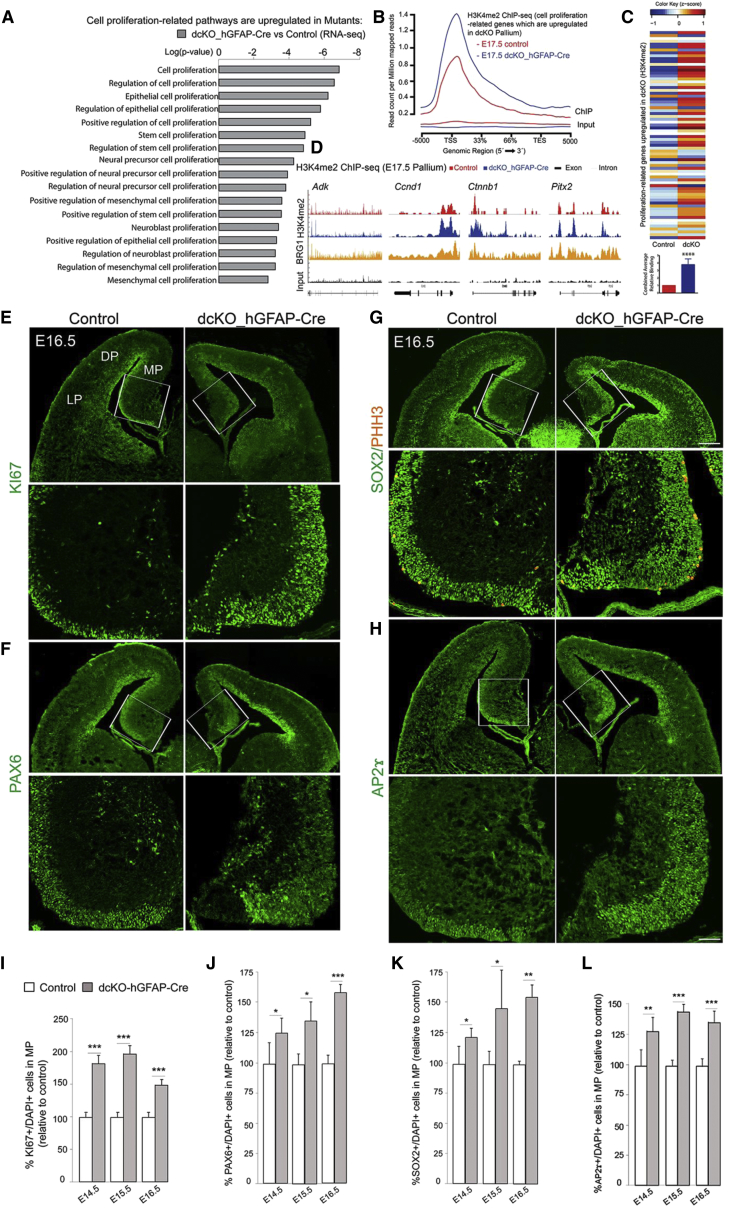
Figure 4.
Loss of BAF155 and BAF170 Causes H3K4me2-Linked Upregulation of Genes Involved in the Mitotic Cell Cycle and Proliferation in Late Cortical Development
(A) Proliferation- and cell-cycle-related genes are upregulated in the dcKO pallium at E17.5.
(B) General H3K4me2 profile plot at proliferation-related genes that are upregulated in dcKO pallium.
(C) Upper panel: heatmap depicting the changes in H3K4me2 levels at proliferation-related genes that are upregulated in dcKO pallium at E17.5. Lower panel: average relative H3K4me2 binding levels on those genes combined.
(D) Integrated genome browser views of H3K4me2 and Brg1 binding (GEO: GSE37151) (Attanasio et al., 2014) along representative proliferation-related genes upregulated in dcKO pallium.
(E–H) Representative images showing IF analyses of coronal sections of control and dcKO pallium at E16.5 using antibodies that specifically label the indicated NSC markers. Lower panels: higher-magnification images of areas indicated by white boxes. Note that a similar image of triple channels for PAX6/TBR2/CASP3 is shown in Figure S6H.
(I–L) Quantitative analyses indicated increased numbers of NSCs in the MP of dcKO mutants at the indicated stages.
Values are presented as means ± SEMs (∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.005; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001). Experimental replicates (n) = 6 (I and L), 4 (J and K). Abbreviations: TSS, transcription start site; TES, transcription end site; MP, medial pallium; DP, dorsal pallium; LP, lateral pallium. Scale bars represent 100 μm (G) and 50 μm (H).