Figure 5.
NE-like Cells in the BAF-Complex-Deleted Pallium in Late Development Retain Their Highly Proliferative Competence
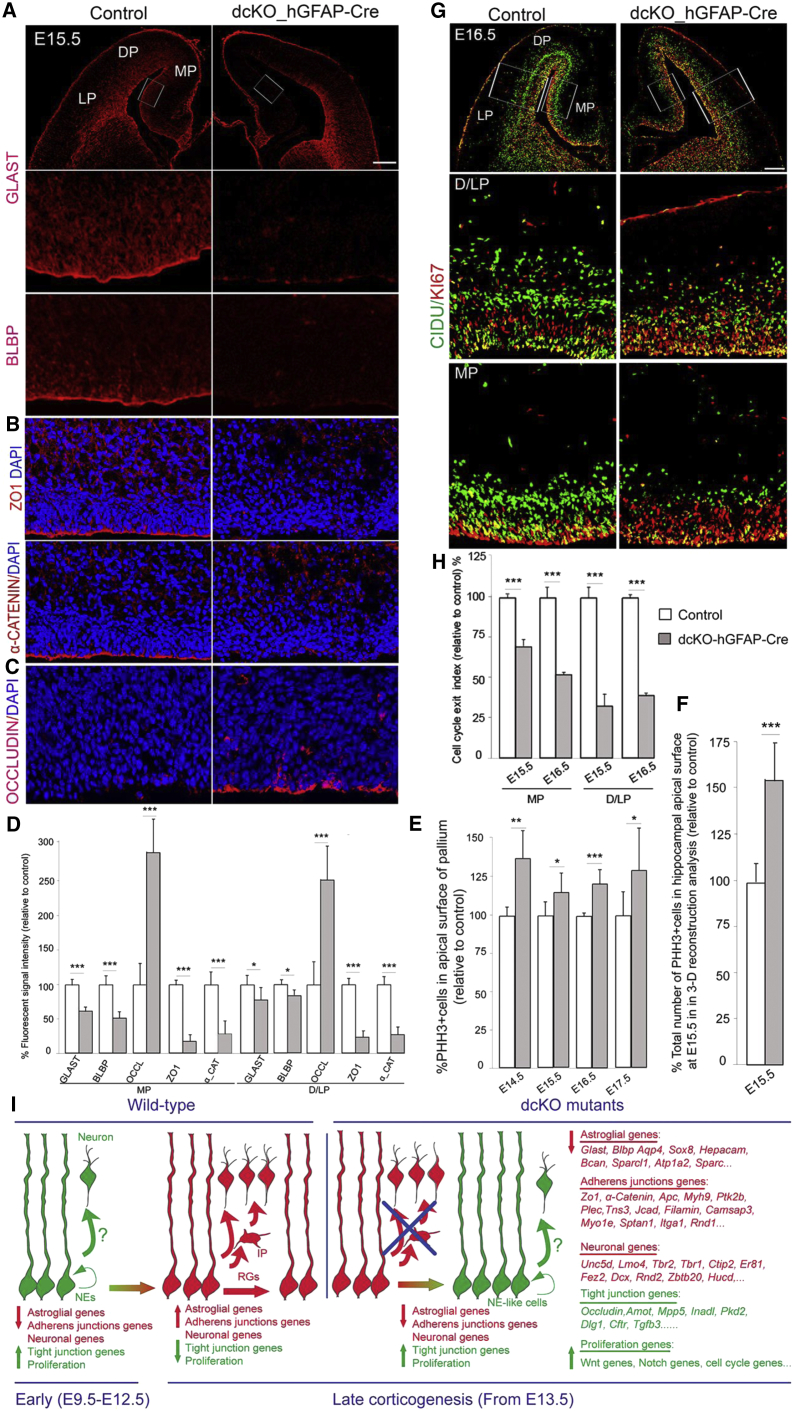
(A–C) Immunostaining of the control and dcKO pallium sections at E15.5 for indicated markers revealed an altered cell identity from GLASThigh+/BLBPhigh+/ZOhigh+/α-Cateninhigh+/OCCLUDIN− RGs in controls to GLASTlow+/BLBPlow+/ZOlow+/α-Cateninlow+/OCCLUDINhigh+ NEs in dcKO MP.
(D) Quantification and statistical analysis of (A)–(C) are shown.
(E and F) Quantitative analyses showing that the loss of BAF155 and BAF170 leads to an increase in mitotic PHH3+ RGs in the pallium at E14.5–E16.5 (E). Note that quantification of PHH3+ cells (F) was done in the entire developing hippocampus (PAX6+/ZBTB20+) at E15.5 using 3D reconstruction (see also Figures S5A and S5B, Video S1).
(G) Images showing double IF at E16.5 for CIDU, and KI67 in control and dcKO mutants.
(H) Quantitative analyses showing a significantly lower exit index (number of CIDU+/KI67- cells per total number of CIDU+ cells) in mutants in D/LP and MP areas than in controls.
(I) Schema illustrating that a higher proportion of RG progenitors in the late-stage (from E13.5) dcKO pallium acquire NE-like identity (i.e., downregulated expression of astroglial, adherens junction, differentiation genes and upregulated expression of tight junction, proliferation genes).
Values are presented as means ± SEMs (∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.005). Experimental replicates (n) = 6 (D and E), 4 (F and H). Abbreviations: NE, neuroepithelial cell; RG, ventricular radial glial progenitors, Hi, hippocampus; Cx, cortex; MP, medial pallium; DP, dorsal pallium; LP, lateral pallium. Scale bars represent 100 μm (A and G).