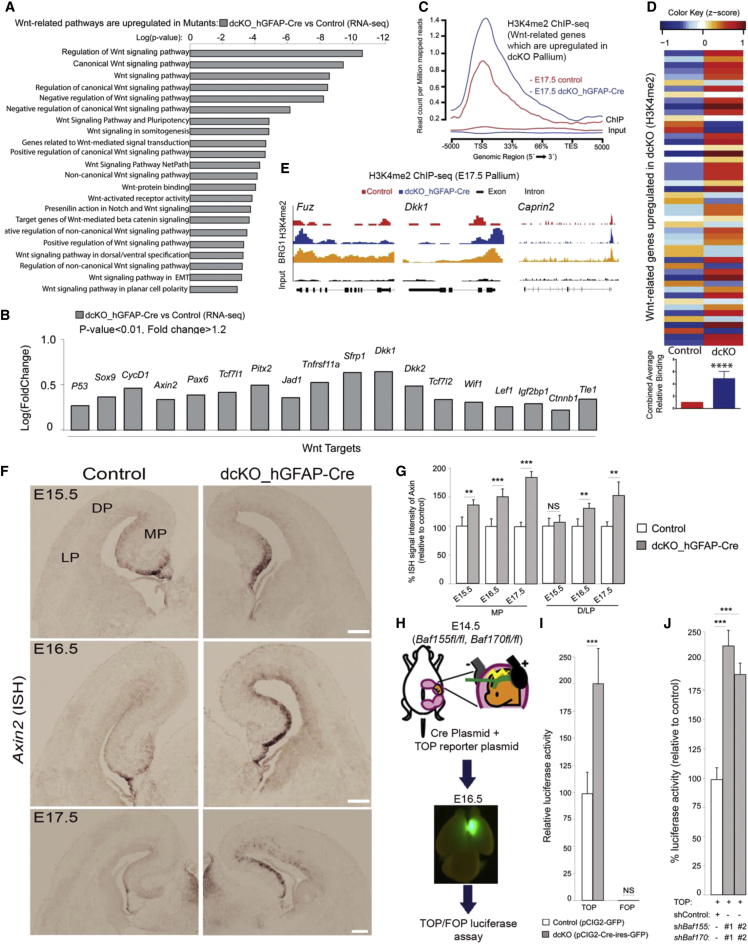
Figure 6.
BAF Complexes Suppress Wnt Signaling Activity
(A) Wnt-related genes are upregulated in the dcKO pallium at E17.5.
(B) Wnt target genes upregulated in the dcKO pallium are shown.
(C) General H3K4me2 profile plot of Wnt-related genes that are upregulated in dcKO pallium.
(D) Upper panel: heatmap depicting the changes in H3K4me2 levels of Wnt-related genes that are upregulated in dcKO pallium at E17.5. Lower panel: average relative H3K4me2 binding levels on those genes combined.
(E) Integrated genome browser views of H3K4me2 and BRG1 binding (GEO: GSE37151) (Attanasio et al., 2014) along representative Wnt-related genes upregulated in dcKO pallium.
(F and G) ISH (F) and quantitative (G) analyses comparing the expression of the Wnt target Axin2 in the control and dcKO pallium at E15.5–E17.5.
(H–J) In vivo (H and I) and in vitro (J) luciferase assay indicating higher Wnt signaling activity in BAF155/BAF170-depleted pallial cells (I) and in Neuro2A cells (J) compared with control cells.
Values are presented as means ± SEMs (∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.005; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001). Experimental replicates (n) = 6 (G and J), 4 (I). Abbreviations: TSS, transcription start site; TES, transcription end site; MP, medial pallium; DP, dorsal pallium; LP, lateral pallium. Scale bars represent 100 μm (F).