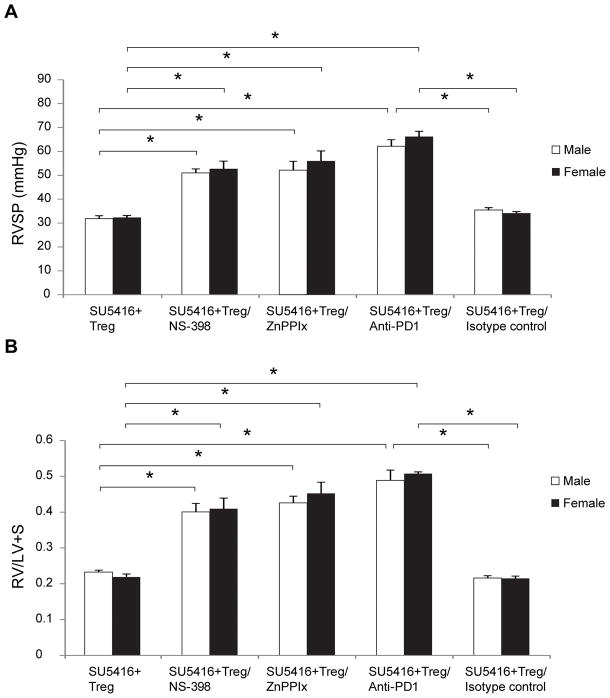
Figure 6. Blocking COX-2, HO-1 and PD-1/PDL-1 signaling pathways abrogates Treg-mediated protection from PH.
(A) RVSP measurements in athymic male and female rats treated with SU5416 + Tregs at d21 and: injected i.p. with NS-398 (a selective COX2 inhibitor)(10mg/kg) daily from day 0 until d21, injected i.p with zinc (II) protoporphyrin IX (ZnPPIX)/HO-1 inhibitor), (40mg/kg) on days 0,2,3,7,14 and 18, injected i.p with anti-PD-1 (PDL-1 ligand) antibody (600mg/kg loading dose) on day 0 with 300mg/kg every other day until d21, injected with isotype control antibody (600mg/kg loading dose) on day 0 and 300mg/kg every other day until d21 (n=4–5 per group). (B) RVH measurements as assessed by RV/(LV+S) ratio in athymic male and female rats treated with SU5416 + Tregs at d21 and: injected i.p. with NS-398 (a selective COX2 inhibitor)(10mg/kg) on day 0 and when daily until d21, injected i.p with zinc (II) protoporphyrin IX (ZnPPIX)/HO-1 inhibitor), (40mg/kg) on days 0,2,3,7,14 and 18, injected i.p with anti-PD-1 (PDL-1 ligand) antibody (600mg/kg loading dose) on day 0 with 300mg/kg every other day until d21, injected with isotype control antibody (600mg/kg loading dose) on day 0 with 300mg/kg every other day until d21 (n=4–5 per group). Data are shown as means with error bars representing SEM (*P<0.05).