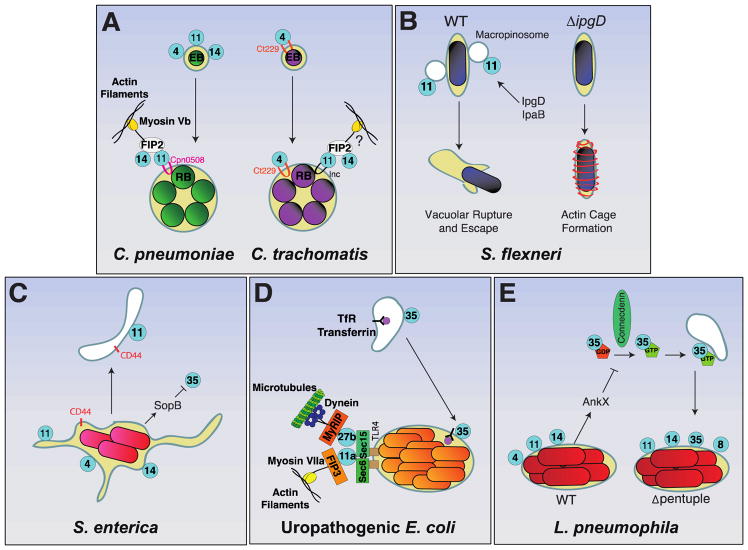
Figure 2. Bacterial pathogens selectively target endocytic recycling Rabs.
A) C. pneumoniae and C. trachomatis – Upon uptake into the host cell, the infectious elementary body (EB) of C. pneumoniae forms the inclusion body. The early inclusion body associates with Rab4, Rab11, and Rab14 through unknown mechanisms. Subsequently, EBs differentiate into the non-infectious replicative bodies (RB). At this later stage the inclusion is associated with Rab11 through direct interaction with the C. pneumoniae inclusion protein Cpn0508. As a result, the Rab11 adaptor proteins Rab11FIP2 (FIP2) is recruited leading to recruitment of Rab14 to the inclusion body and interaction with the actin motor protein Myosin Vb. The developmental cycle of infection of C. trachomatis is similar to C. pneumoniae. Rab4 is recruited to the early inclusion by the C. trachomatis inclusion protein CT229. The Rab11-FIP2-Rab14 complex is also recruited to the inclusion body, but it is unclear if it facilitates interactions with the cytoskeleton.
B) S. flexneri – The nascent vacuole containing S. flexneri associates with Rab11-positive macropinosomes. Recruitment of macropinosomes is critical for vacuolar rupture and escape of S. flexneri into the cytosol. The effector protein IpgD, a PI(4,5)P2 phosphatase, is responsible for recruitment of Rab11-positive macropinosomes to the invasion site. In the absence of IpgD, Rab11-positive macropinosomes are not recruited and instead the vacuole becomes enclosed in an actin cage. S. flexneri effector IpaB is thought to directly bind cholesterol to induce formation of Rab11 positive compartments while the bacterium enters a replicative state.
C) S. enterica serovar Typhimurium – replicates within the Salmonella-containing vacuole (SCV). The SCV matures to resemble a late endosome, but does not fuse with lysosomes. The SCV interacts with endocytic recycling pathways through the early recruitment of Rab4 and Rab11. The cell adhesion molecule CD44 is recycled from the SCV back to the plasma membrane through a Rab11-dependent pathway. The effector SopB, a PI(4,5)P2 phosphatase, prevents Rab35 recruitment to the SCV by modifying the SCV’s surface charge.
D) Uropathogenic E. coli – can reside within a vacuole that co-localizes with Rab35 and the transferrin receptors, a major transporter of iron within the host cell. UPEC is also capable of being expelled from the cell without damage to the bacterium or the host. TLR4 present on the vacuole interacts with Sec6 and Sec15 which recruit Rab11a and Rab27b to the UPEC-containing vacuole. Rab11a can then bind its adaptor protein Rab11FIP3 (FIP3) to recruit the actin motor protein Myosin VIIa while Rab27b recruits the microtubule motor protein dynein through its adaptor protein MyRIP.
E) L. pneumophila – The Legionella-containing vacuole (LCV) associates with Rab4a, Rab11a and Rab14 through an unknown mechanism. The effector protein AnkX phosphocholinates Rab35 preventing activation by the cognate GEF, Connecdenn, and thereby inhibiting Rab35 activation. A mutant of L. pneumophila missing five of its genomic islands encoding effector proteins (Δpentuple) still recruited Rab4a, Rab11a and Rab14 and did not prevent Rab35 recruitment.