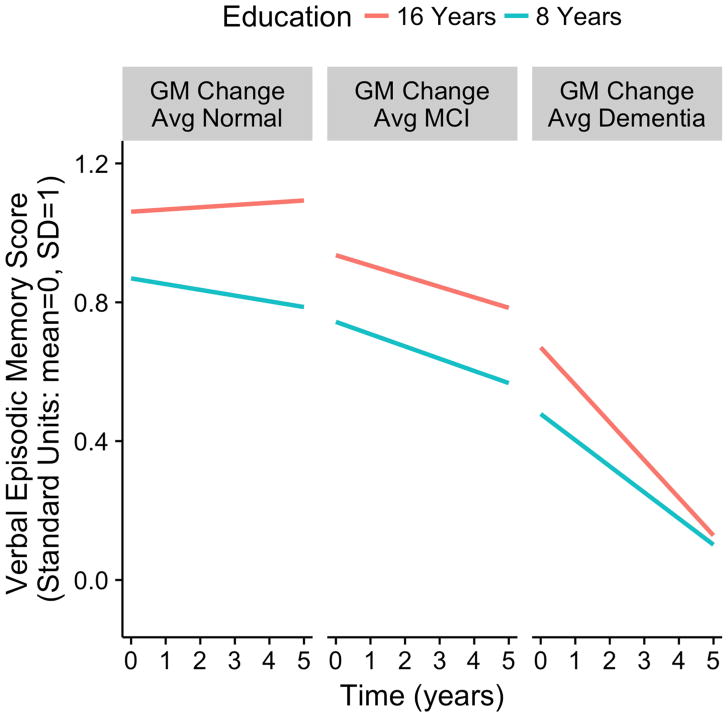
Figure 2.
Expected 5-year longitudinal trajectories for verbal episodic memory scores for specific education levels (8 and 16 years) and specific brain atrophy values (average atrophy rates in this sample for Normal, MCI, and Dementia groups). Estimated model parameters were used to demonstrate the effects of education, brain atrophy, and their interaction on longitudinal change in this one specific cognitive outcome. The education by gray matter change interaction effect on rate of cognitive decline was stististically significant (p<0.001).