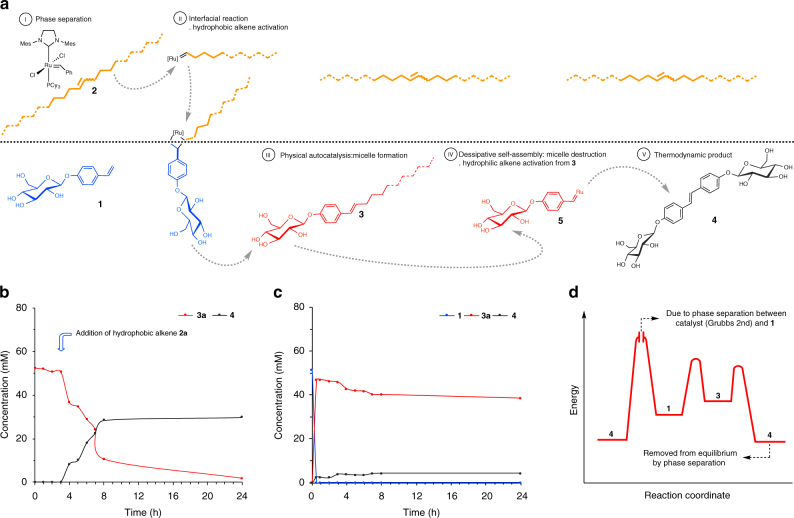
Fig. 4.
Mechanistic hypothesis supported by control experiments. a Diagram of the dynamic system including the chemical structures involved. Kinetic analysis representing concentration vs. time of 1 (blue), 3a (red) and 4 (black) for the control experiments: b In D2O replicator 3a is stable. It is only on addition of alkene 2a that it is fully consumed to form waste product 4. c In reaction between 1 and 2a performed under homogeneous conditions no autocatalytic kinetics are observed for the formation of 3a. Under these conditions product 3a appears to be relatively stable. d Qualitative energy profile of the system, highlighting the higher effective barrier for direct conversion of 1 to 4 under phase separated conditions. Phase separation may shift the equilibrium position between 3a and 4 by effectively removing water soluble 4 from the micellar environment