Abstract
Gene editing can be used to overcome allo-recognition, which otherwise limits allogeneic T cell therapies. Initial proof-of-concept applications have included generation of such “universal” T cells expressing chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) against CD19 target antigens combined with transient expression of DNA-targeting nucleases to disrupt the T cell receptor alpha constant chain (TRAC). Although relatively efficient, transgene expression and editing effects were unlinked, yields variable, and resulting T cell populations heterogeneous, complicating dosing strategies. We describe a self-inactivating lentiviral “terminal” vector platform coupling CAR expression with CRISPR/Cas9 effects through incorporation of an sgRNA element into the ΔU3 3′ long terminal repeat (LTR). Following reverse transcription and duplication of the hybrid ΔU3-sgRNA, delivery of Cas9 mRNA resulted in targeted TRAC locus cleavage and allowed the enrichment of highly homogeneous (>96%) CAR+ (>99%) TCR− populations by automated magnetic separation. Molecular analyses, including NGS, WGS, and Digenome-seq, verified on-target specificity with no evidence of predicted off-target events. Robust anti-leukemic effects were demonstrated in humanized immunodeficient mice and were sustained longer than by conventional CAR+TCR+ T cells. Terminal-TRAC (TT) CAR T cells offer the possibility of a pre-manufactured, non-HLA-matched CAR cell therapy and will be evaluated in phase 1 trials against B cell malignancies shortly.
Keywords: B-ALL, CAR T cells, CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing, lentiviral vector gene therapy
Georgiadis et al. combine a lentiviral chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) vector with CRISPR guides incorporated into the 3′ LTR with transient Cas9 mRNA delivery for coupled gene modification effects. Processing through an automated platform to remove residual TCRαβ-cells was scalable and yielded highly enriched “universal” T cells with potent anti-leukemic effects.
Introduction
T cells engineered to express recombinant antigen-specific receptors or chimeric antigen receptors are in multi-phase trials, with some approaches yielding compelling remission effects against refractory leukemia.1 The majority of subjects treated to date have provided and received autologous T cells, but this approach may not be best suited for widespread cost-effective delivery of cellular therapy. Gene editing offers the prospect of addressing human leukocyte (HLA)− barriers and the development of universal T cell therapies.2, 3 Recently, T cells modified using transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs) and expressing chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) against CD19 have been used to treat refractory relapsed B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) in infants.4 These “off the shelf” cells were derived from a non-HLA-matched donor and were disrupted for CD52 expression to evade the depletion effects of alemtuzumab and were simultaneously modified at the T cell receptor (TCR) alpha chain constant (TRAC) region and depleted of T cells expressing TCRαβ to reduce the risk of graft versus host disease (GVHD).5 Clinical trials are underway to assess the strategy further in children and adults and key aspects determining dosing schedules related to carriage of residual TCRαβ T cells and the proportion of cells expressing CAR19. The former comprise less than 1% of the total cell inoculum after TCRαβ magnetic bead depletion but constitute a risk for GVHD and are strictly capped to below 5 × 104 T cells/kg.6 This, in turn, limits the total cell dose, and because only a proportion of cells express CAR19 as a result of batch-to-batch variation in lentiviral transduction efficiency, the total cell dosing regimen differs between batches. Similar issues arise for other gene editing platforms relying on segregated DNA nuclease delivery, whether by non-integrating viral delivery of zinc-finger nucleases3 or megaTALs combined with non-viral delivery.7
We designed a self-inactivating (SIN) lentiviral platform that coupled transgene expression with CRISPR editing effects for efficient and homogeneous T cell modification (Figure 1A) and demonstrated that this system is scalable and can be incorporated into a largely automated manufacturing process. CRISPR-mediated effects in CAR19-modified T cells have been reported previously. For example, Ren et al.8, 9 used CRISPR RNA electroporation to disrupt endogenous TCR and β2-microglobulin (B2M) genes for disruption of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I in T cells transduced with a lentiviral CAR vector, but editing and transgene effects were unlinked. Other lentiviral configurations have incorporated both CRISPR guide sequences and Cas9 expression cassettes that become integrated into the target cell genome as a constituent of proviral vector DNA.10 Although suitable for pre-clinical studies, constitutive expression of Cas9 would be problematic in human trials, not the least because of its bacterial origin and likely immunogenicity. To overcome this issue, we delivered capped, polyadenylated, uridine-modified Cas9 mRNA by electroporation to T cells that had been transduced with our “terminal-CRISPR” lentiviral configuration. Here, CAR19 was expressed under the control of an internal human promoter, and CRISPR guide sequences and associated H1/U6 promoters were incorporated into the U3 region of the 3′ long terminal repeat (LTR) sequence of the vector. Previous vector configurations using these flanking regions have included a γ-retroviral vector for expression of cDNA cassettes11 and a lentiviral system encoding short hairpin RNA interference elements.12 Modification of the LTR can impair retroviral titers but has a number of advantages, including avoiding interference with internal promoters13 and duplication of sequences cited in the U3 locus following reverse transcription. Here we adopt and refine this approach for CRISPR delivery, anticipating guide duplication and incorporation into the 5′ LTR during reverse transcription and vectorized linkage of guide effects with transgene expression. We demonstrate compliant scalability and the potential of the platform for the generation of “universal” human T cells on a clinical scale. Potent anti-leukemic effects of TCR-depleted CAR19 T cells were demonstrated in a human:murine chimeric tumor model. Multi-modal analysis confirmed highly efficient “on-target” modifications with no predicted or unpredicted “off-target” events recorded.
Figure 1.
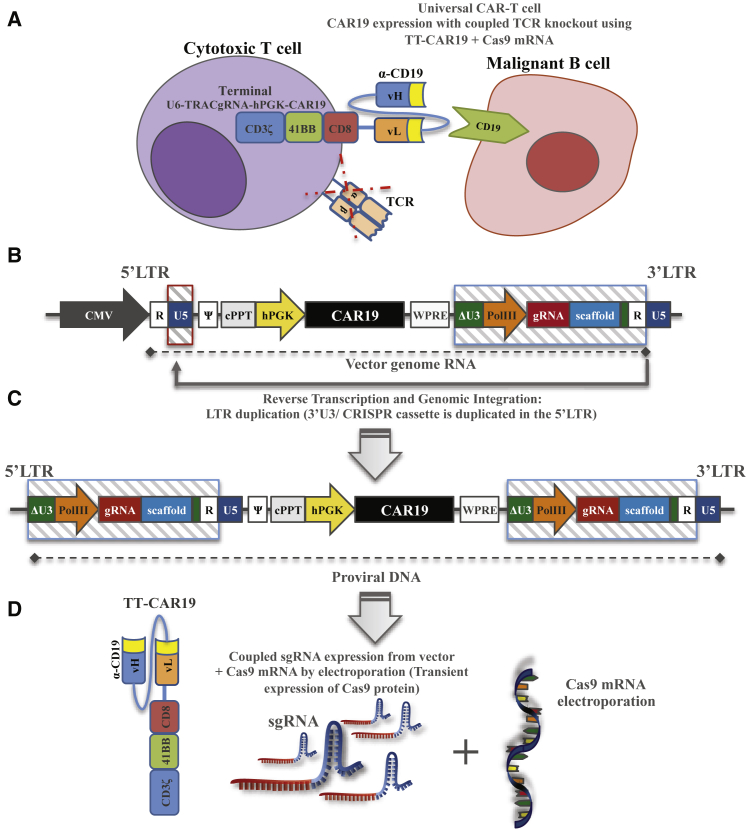
Terminal CRIPSR-CAR-Coupled Lentiviral Vector Configuration
(A) Schematic of CAR 19 expression for the targeted killing of CD19+ B cells with simultaneous CRISPR mediated TCR disruption, where ideally all T cells are CAR19+ and TCR−. (B) Self-inactivating lentiviral plasmid configuration coupling terminal TRAC (TT) CRISPR guide RNA and CAR19 transgene expression and a human Pol III promoter-sgRNA CRISPR cited in the deleted unique (ΔU3) region, proximal to repeat (R) elements of the 3′ long terminal repeat (LTR). (C) Following reverse transcription, 3′ LTR elements, including the Pol III-sgRNA cassette, duplicate to the 5′ LTR of the proviral vector. (D) Single guide RNA (sgRNA) expressed from both 5′ and 3′ LTR vector elements forms ribonucleoprotein complexes with Cas9 following electroporation of Cas9 mRNA, and this effect is restricted to transduced populations. CMV, cytomegalovirus promoter; hPGK, human phosphoglycerate kinase promoter; cPPT, central polypurine tract; WPRE, woodchuck post-transcriptional regulatory element; gRNA, guide RNA; vH/vL, variable heavy or light chain; TCR, T cell receptor.
Results
Design and Construction of Lentiviral Terminal-TRAC Guide RNA Vectors
Incorporation of a Pol III promoter and single guide RNA (sgRNA) sequence into the 3′ LTR of a U3-deleted third-generation lentiviral vector generated a self-duplicating CRISPR expression cassette (Figure 1B). A region immediately proximal to 3′ repeat (R) regions was selected to preserve reverse transcription-mediated duplication to the 5′ LTR, resulting in a proviral form with both 5′ and 3′ flanking terminal CRISPR elements (Figure 1C). For targeting of endogenous TCR expression, a sgRNA sequence targeting the TRAC locus (specificity score 94/10014) was placed under the control of the human Pol III promoter, U6, followed by a sgRNA sequence specific for S. pyogenes Cas9, which was delivered separately as mRNA by electroporation (Figure 1D). The lentiviral vector encoded a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR19) under the control of an internal human phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) promoter. The concentrated vector titer of this “Terminal-TRAC” (TT) configuration (TT-hPGK-CAR19) was comparable with a conventional pCCL-hPGK-CAR19 vector (1.6 × 108/mL versus 1.5 × 108/mL), indicating that inclusion of the sgRNA cassette in the 3′ LTR was not detrimental to vector titer and supported comparable transduction efficiencies in primary T cells. Unique primer pairs amplified both 3′ and 5′ LTR regions in these cells (Figure 2A) and yielded the expected 392-bp 3′ U5 reaction product from the pCCL-hPGK-CAR19-transduced cells compared with a larger 755-bp product from the TT-hPGK-CAR19-transduced cells. A 742bp 5′ PCR product indicated duplication of the U6 promoter-sgRNA-scaffold sequences in contrast to a 379-bp conventional duplication product. Bands were extracted, and sequences were verified by Sanger sequencing. Furthermore, qRT-PCR found that guide RNA expression peaked between 24 and 72 hr after lentiviral transduction and thereafter remained stable during manufacture (Figure 2B).
Figure 2.
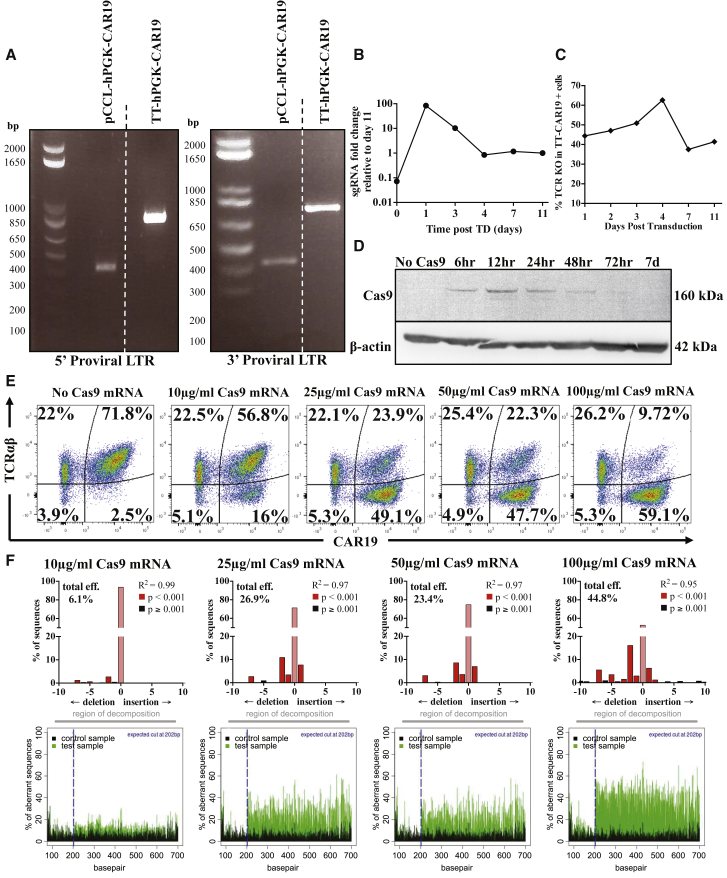
Validation of the Terminal CRISPR-CAR Vector and Titration of the Cas9-Mediated Knockout Effect in Primary Human T Cells
(A) PCR amplification of proviral 5′ LTR elements spanning the ΔU3 and Psi regions (755-bp band) and 3′ LTR (742-bp band) confirmed the presence of duplicated Pol III-sgRNA in T cells transduced with TT-CAR19. (B) qRT-PCR measurement of the TRAC sgRNA fold change 0, 1, 3, 4, 7, and 11 days after transduction shows stabilization of sgRNA expression after 4 days. (C) Quantification of TCR knockout following Cas9 mRNA electroporation of primary T cells 1, 2, 3, 4, 7, or 11 days after TT-CAR19 transduction, showing optimal TCR disruption occurring at the 3- to 4-day time point. Percent knockout was calculated by flow cytometry-based detection of TCR expression in the CAR19+ population. (D) Following Cas9 mRNA electroporation, Cas9 protein expression detected as a 160-kDa band peaked after 12 hr and became undetectable by 72 hr. β-Actin detection (42 kDa) verified protein loading. (E) Coupling of transgene expression and TCR disruption effects across a gradient of Cas9 mRNA concentrations in TT-CAR19-transduced PBMCs exhibiting more than 70% CAR19 expression. (F) PCR amplification and analysis by TIDE algorithm for the detection of NHEJ signatures across the TRAC locus confirmed Cas9 dose-dependent scission and repair effects.
Transient Cas9 mRNA Delivery by Electroporation to TT-CAR T Cells
Previous lentiviral configurations have incorporated Cas9 expression cassettes, but this could promote immunogenicity and result in on-going scission effects, risking toxicity. Stabilized Cas9 mRNA (capped, polyadenylated, and uridine-modified) was delivered by electroporation for transient effects in dividing T cells exposed to a single round of transduction with the TT-hPGK-CAR19 vector. An interval of 3 days was found to be optimal for TRAC disruption (Figure 2C). Cas9 protein was detected by western blot as a 160-kDa protein band, with peak expression 12 hr after mRNA electroporation and clearance by 72 hr (Figure 2D). Titration of Cas9 mRNA-mediated disruption of TCR expression exhibited saturation above 25 μg/mL (Figure 2E). Molecular signatures of non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) at the TRAC locus were confirmed by PCR sequencing across the target locus and TIDE analysis of the 772-bp TRAC amplicon (Figure 2F). Crucially, almost all cells expressing CAR19 were found to have disrupted TCR expression, indicating that CRISPR-Cas9 effects were coupled to transgene expression.
Scalability of TT-CART Cell Production
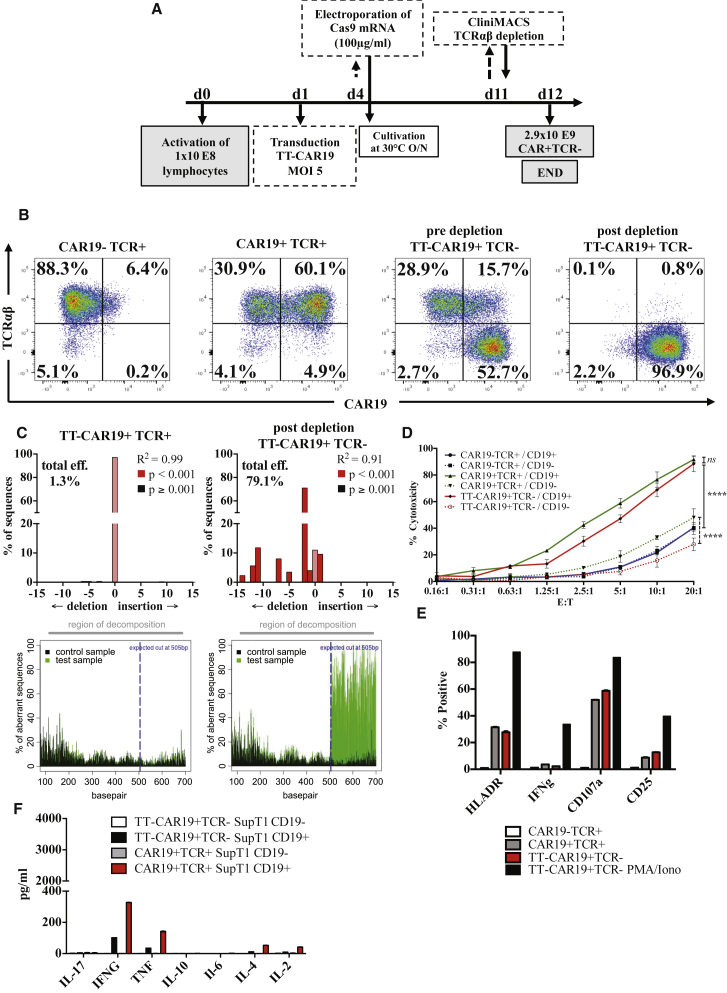
A critical hurdle for CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing is scalability and compliance for therapeutic manufacturing. We adapted an automated T cell lentiviral transduction procedure using the CliniMacs Prodigy system to compare alongside conventional cultures in G-Rex flasks and activated 1 × 108 lymphocytes from a thawed leukapheresis harvest ahead of lentiviral transduction with the TT-hPGK-CAR19 vector at MOI 5 in the closed system tubing set (Figure 3A; Figure S1). After a further 72 hr, cells were removed from the device and electroporated with Cas9 mRNA, after which the cells were returned to the CliniMACS Prodigy and cultured overnight at 30°C. After 11 days, CAR19 expression was 62% in CD45+CD2+ cells, and TCR knockout in CD45+CD2+CAR19+ cells was 77% (Figure 3B). Further processing by magnetic bead-mediated depletion of residual TCRαβ cells yielded a highly purified population of TCR-depleted cells (>99%), almost all (96.9%) of which were CAR19+ T cells with a vector copy number (VCN) of 1.69 (Figure 3B). Disruption of the TRAC locus at the genomic level was verified by TIDE PCR (Figure 3C), which revealed NHEJ events of around 80%, with next-generation sequencing (NGS) detecting on-target cleavage effects in 92% of sequence reads. Overall, a final cell yield of 2.9 × 109 TT-CAR19+TCR− T cells was produced, almost 30 times the starting number, sufficient to create therapeutic doses for over 20 average adult subjects.
Figure 3.
Scalability and In Vitro Functional Integrity of TT-CAR19+TCR− T Cells
(A) Scaled manufacture of homogeneous TT-CAR19+TCR− cells using a semi-automated process on a CliniMACS Prodigy device in combination with off-device electroporation. Control cultures were separated and cultured in G-Rex 10 flasks at relevant stages. Following anti-CD3/anti CD28 activation, lentiviral transduction, and Cas9 mRNA electroporation, T cells were expanded in the integrated cultivation chamber before magnetic bead depletion of residual TCRαβ cells. As a consequence, coupled TCR knockout effects and CAR expression were assured in the final product. (B) Flow cytometry of untransduced (UTD) cells and cells transduced with TT-CAR19 but not supplied with Cas9 provided comparator data. Addition of Cas9 mRNA by electroporation resulted in TCR loss in more than 52% of cells, and this population was enriched to more than 99% by TCRαβ depletion using magnetic beads. The resulting population was more than 97% CAR19+. (C) PCR amplification and analysis by TIDE algorithm of the TRAC locus in TT-CAR19 T cells with and without Cas9 mRNA electroporation, confirming on-target NHEJ repair signatures. (D) Comparable CD19-specific cytotoxicity against 51Cr-labeled CD19+ SupT1 cells across a range of CAR19+ effector-to-target ratios was detected for CAR19+TCR+ (green) and TT-CAR19+TCR− effectors (red) (p = 0.4461) but not for UTD CAR19−TCR+ populations (blue) (p < 0.0001), indicating intact effector function after the additional processing steps required to generate universal cells. CD19− control targets confirmed specificity (dotted lines) (p < 0.0001). Error bars represent SEM (n = 3). Linear regression analysis showed significance between CAR19−TCR+ and CAR19+TCR+ (F = 70.37, degrees of freedom numerator [DFn] = 1, degrees of freedeom denominator [DFd] = 36, p < 0.0001) or TT-CAR19+TCR− (F = 47.65, DFn = 1, DFd = 44, p < 0.0001) effectors against CD19+ SupT1 targets. No significance was seen between CAR19+TCR+ and TT-CAR19+TCR− effectors (F = 0.59, DFn = 1, DFd = 36, p = 0.45). (E) CD107a degranulation responses detected by flow cytometry were also comparable in CAR19+TCR+ and TT-CAR19+TCR− effectors when co-cultured with CD19+ Daudi targets. Phorbol 12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA) and ionomycin stimulation of TT-CAR19+TCR− effectors served as positive controls for the detection of HLA-DR, IFNγ, CD107a, and CD25. Error bars represent SEM of technical replicates (n = 3). (F) Flow cytometric detection of cytokines in supernatant from co-cultures with SupT1 targets found comparable levels of IFNγ and TNF-α for CAR19+TCR+ and TT-CAR19+TCR− effectors. Error bars represent SEM of technical replicates (n = 3).
TT-CAR19+TCR− T Cells Efficiently Target CD19+ Cells In Vitro
The cytolytic potential of TT-CAR19+TCR− cells was assessed by in vitro cytotoxicity against 51Cr-loaded CD19+ or CD19− SupT1 target cells. When normalized for CAR19+ cells, both TT-CAR19+TCR− cells and CAR19+TCR+ T cells exhibited comparable specific lysis of CD19+ SupT1 targets after 4 hr of co-culture, in contrast to non-transduced CAR19−TCR+ control cells (p < 0.0001) (Figure 3D). Specific lysis of another CD19+ tumor line, Daudi, was also documented for CAR19+TCR+ and TT-CAR19+TCR− effectors, and a 4-hr degranulation assay on this target cell line further corroborated the cytotoxicity data, with 57% of CAR19+TCR− and 53% of CAR19+TCR+ cells upregulating CD107a expression (Figure 3E). Finally, a cytometric bead array (CBA) assay recorded slightly increased cytokine production of interferon γ (IFNγ), tumor necrosis factor (TNF), interleukin-4 (IL-4), and IL-2 after 24 hr of co-culture with CD19+ SupT1 cells but not CD19-SupT1 cells, further confirming the target-specific effect (Figure 3F).
Characterization of On- and Off-target CRISPR Effects
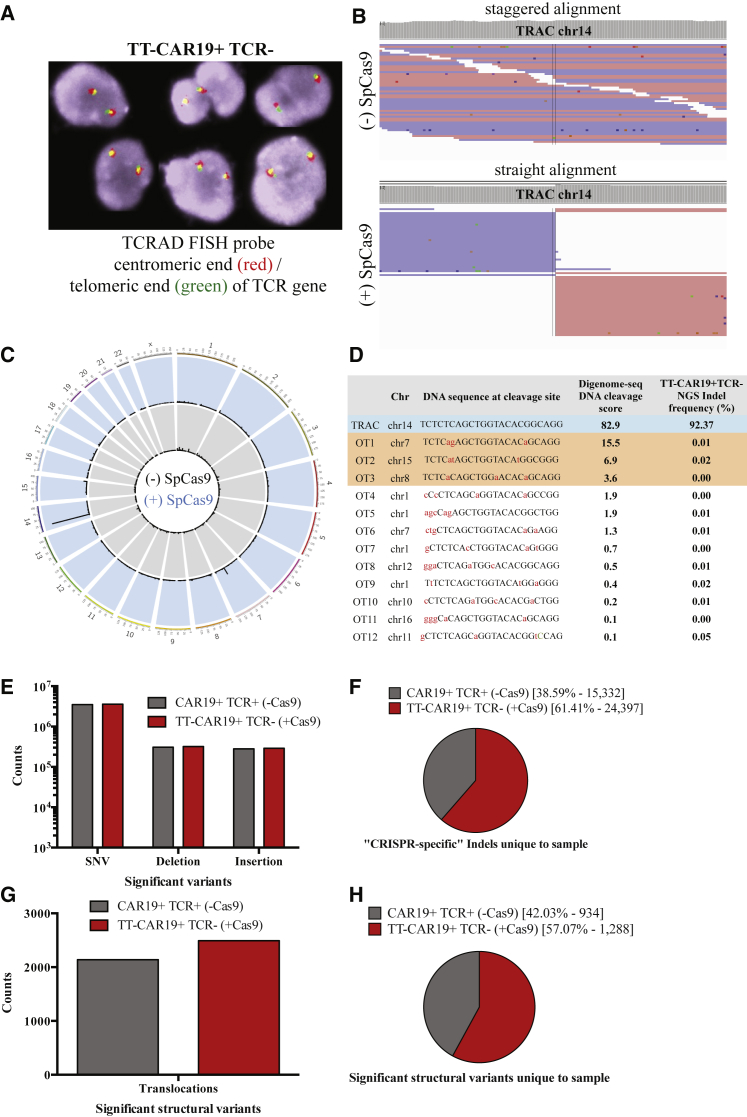
Previously, we reported that T cells modified with a combination of TRAC- and CD52-specific TALENs exhibited translocation events involving the TRAC locus in around 4% of 500 interphase spreads using a dual-color break-apart fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) probe for the TRAD locus (which incorporates the TRAC site).4 For TT-CAR19+ T cells, no breakpoints were identified within the sensitivity limits of the assay across 350 interphase spreads in Cas9-treated cells and across 600 interphase spreads in non-treated cells (Figure 4A). Further investigations compared these two populations using three independent modalities based on whole-genome sequencing (WGS), targeted NGS, and Digenome-seq. Predicted on-target insertion or deletion (indel) modifications captured by Digenome-seq had a score of 82.9%, corroborated by targeted amplification of the TRAC locus and analysis of more than 35,000 reads by NGS, which revealed an indel frequency of 92.3% versus 0.00% in non-edited cells (Figures 4B and 4C; Table S1; Figure S2). In comparison, estimates by TIDE-PCR and 30× WGS had yielded lower modification efficiencies of 79% and 54%, respectively, reflecting less informed analysis techniques and lower read depths. Comparing events at 49 in silico predicted off-target sites by WGS and NGS and across ten additional gene loci with 14q translocation phenomena known to be associated with T cell leukemias (TAL1, LCK, REL, MYC, NOTCH1, TLX1, THUMPD1, BCL11B, TCL1A, and TCL1B), there were no notable differences between the modified and non-modified samples (Table S1). In addition, Digenome-seq captured a further 12 off-target sites, of which 8 were distinct, not having been predicted in silico, with 3 of 12 showing DNA cleavage scores between 3.5%–16% (Figures 4C and 4D; Table S2). However, further NGS-based interrogation of these 12 sites in TT-CAR19+TCR− DNA did not detect genomic disruption (Figure 4D; Table S2). Wider, unbiased genomic variant calling using read frequency-based significance thresholding on WGS data identified a comparable number of single nucleotide variants (SNVs), insertions, and deletions in both Cas9-treated and non-treated cells (Figure 4E).
Figure 4.
Off-Target Analysis by FISH, Digenome-Seq, and WGS
(A) TRAD FISH probe (Cytocell) – red centromeric end – green telomeric end of the TRAC gene. Two fusions (green/red) present showed no rearrangement of the TRAD locus in TT-CAR19+TCR−(+Cas9)-treated samples. (B) Digenome-seq captured on-target cleavage of the TRAC locus, chr14. Straight alignment in TRAC sgRNA SpCas9-digested DNA indicated on-target cleavage of the TRAC locus compared with staggered alignment of untreated DNA. (C) On- and off-target capture by Digenome-seq in TRAC sgRNA SpCas9-treated DNA displaying on-target cleavage (chr14) and off-target events in chr7 and chr15. (D) Cleavage scores in 12 chromosomal locations captured by Digenome-seq as off targets in TRAC sgRNA SpCas9-treated DNA. High-resolution NGS-based validation of captured off-target sites in TT-CAR19+TCR− DNA shows absence of off-target indels. (E) Genomic variants (SNVs, deletions, and insertions) identified by 30× WGS and classed as significant by frequency of detection showed comparable counts in both CAR19+TCR+(−Cas9)-treated and TT-CAR19+TCR−(+Cas9)-treated samples. (F) CRISPR-specific indels identified to be unique to each sample exhibit a higher frequency in the edited TT-CAR19+TCR−(+Cas9) sample. (G) Comparative frequency of structural variant (translocations) counts considered to be significant (at least 2 supporting reads) after 30× WGS analysis in CAR19+TCR+(−Cas9)-treated and TT-CAR19+TCR−(+Cas9) samples. (H) Translocations unique to each sample as part of total reads (F) reveals a minor increase in the TT-CAR19+TCR−(+Cas9)-treated sample.
Further analysis of “CRISPR-specific” mutations in the WGS data, which considered sequences proximal to PAM motifs, found that 61% of indels were unique to TT-CAR19+TCR− Cas9-treated samples compared with 39% of changes in non-treated cells (Figure 4F). Similarly, the translocation frequency was comparable in both samples (Figure 4G), with 57% of structural unique variants detected in Cas9-treated cells and 42% in non-treated samples (Figure 4H). Additional filtering of these sites identified 16 Cas9-treated and 14 non-treated changes as precise changes. Interestingly, one unpredicted site appeared to have been the subject of unanticipated modification. Chr3:128630177-128630178, encoding RPN1, was found to have a 15% frameshift-associated indel frequency (8 of 50 reads) compared with 0 of 33 control sample reads. This site was not identified by Digenome-seq analysis, and further interrogation of the RPN1 locus by NGS discounted these indels, highlighting the limitations of low-depth sequencing and emphasizing the need for multifaceted investigations. Importantly, at the cellular level, T cell function was preserved, and there was no evidence of overt toxicity in the edited TT-CAR19+TCR− product.
TT-CAR T Cell Anti-leukemic Activity In Vivo
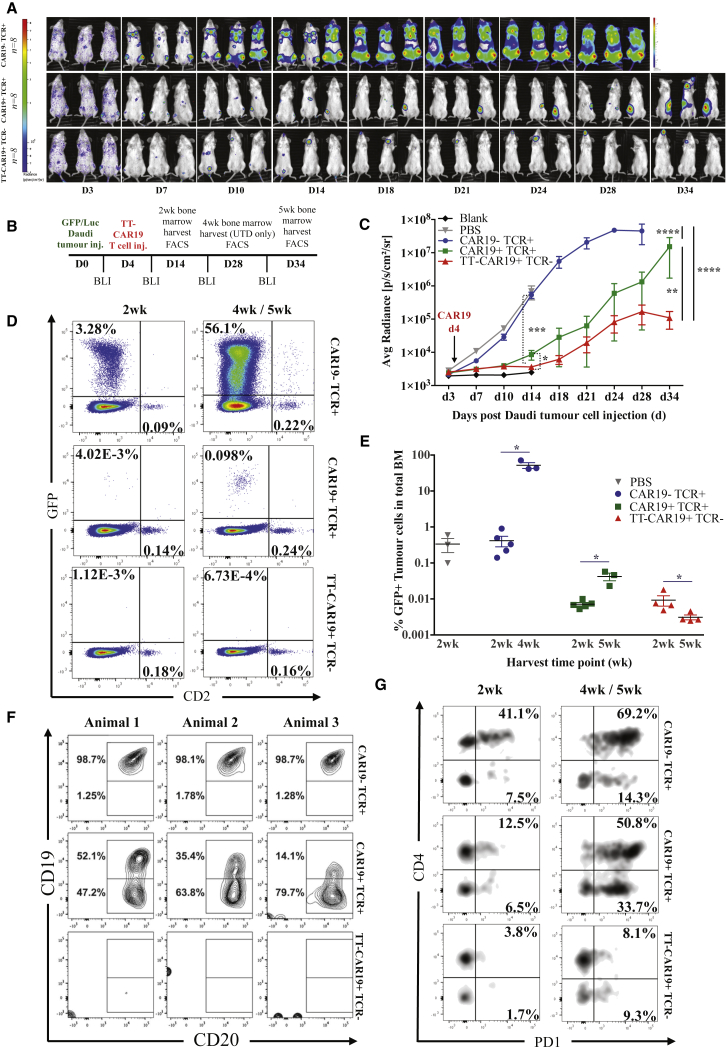
A humanized murine model of leukemic clearance was used to assess in vivo function of engineered CAR19 T cells. Non-obese diabetic (NOD)/severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID)/γc−/− (NSG) mice inoculated intravenously with 5 × 105 CD19+EGFP+luciferase+ Daudi cells were imaged after 3 days and then, in groups of 8 animals, injected with either TT-CAR19+TCR−, CAR19+TCR+, or untransduced CAR19−TCR+ effector cells. Serial bioluminescence imaging was performed on days 7, 10, and 14, and half of the animals were then tracked for a further 14–21 days (Figures 5A and 5B). There was rapid clearance of tumors in groups receiving CAR19+ T cells, with negligible signal by day 14, in contrast to mice receiving non-transduced T cells or PBS (***p < 0.001) (Figure 5A). Interestingly, TT-CAR19+TCR− (n = 8)-mediated clearance by day 14 was superior compared with clearance in CAR19+TCR+ T cell-injected mice (n = 8) (*p < 0.05) based on bioluminescence quantification (Figure 5C). Flow cytometric analysis was undertaken for GFP+ Daudi cell and CD45+CD2+ effector T cell populations harvested from bone marrow of mice injected with TT-CAR19+TCR− (n = 4 of 8), CAR19+TCR+ (n = 5 of 8), CAR19−TCR+ (n = 5 of 8), and PBS (n = 3 of 3). By day 14, less than 0.01% (0.009% ± 0.006%) of total marrow harvested from long bones of mice injected with TT-CAR19+TCR− and < 0.007% ± 0.002% of CAR19+TCR+-injected mice expressed GFP Daudi cells, indicating a highly significant (>45-fold) reduction compared with the 0.416% ± 0.301% (*p < 0.05) and 0.336% ± 0.246% tumor content detected in the marrow of CAR19−TCR+ and PBS control animals, respectively (Figure 5E).
Figure 5.
Human:Murine Leukemia Responses by TT-CAR19+ Effector T Cells against CD19+GFP/Luciferase Daudi Targets
(A) Serial bioluminescence imaging (BLI) of NSG mice following intraperitoneal administration of D-luciferin substrate. (B) Timeline of tumor and effector cell injection, BLI, and organ harvest time points over the 5-week period. (C) Progressive increases in radiance (p/s/cm2/sr) in non-treated (n = 3) or control CAR19−TCR+ (n = 8) effector groups indicated leukemic progression within 2 weeks and resulted in death by 4 weeks of the three animals subjected to extended monitoring. Mice injected with CAR19+TCR+ (n = 8) or TT-CAR19+TCR− (n = 8) effectors exhibited significantly delayed leukemic progression by 2 weeks compared with CAR19−TCR+ (p = 0.0002), as tracked for 5 weeks in three animals with CAR19+TCR+ and four with TT-CAR19+TCR− cells. The latter exhibited the lowest disease radiance at termination; p < 0.0001, error bars represent SEM. Linear regression analysis showed significance among all groups: CAR19+TCR+ versus CAR19−TCR+ (F = 29.79, DFn = 1, DFd = 87, p < 0.0001), TT-CAR19+TCR− versus CAR19−TCR+ (F = 53.77, DFn = 1, DFd = 92, p < 0.0001), and TT-CAR19+TCR− versus CAR19+TCR+ (F = 8.93577, DFn = 1, DFd = 95, p = 0.0036). Dotted lines represent Mann-Whitney U test (*p = 0.0499, ***p = 0.0002). (D) Representative flow cytometry plots gated on human CD45+ populations in bone marrow (BM), demonstrating a greatly reduced but well demarcated population of GFP+ leukemia in CAR19+TCR+-treated mice (n = 5 [2 weeks]/n = 3 [5 weeks]) compared with the UTD CAR19−TCR+ cohort (n = 5 [2 weeks]/n = 3 [4 weeks]). In contrast, leukemia was barely detectable in TT-CAR19+TCR−-treated animals (n = 4 [2 weeks]/n = 4 [5 weeks]). Human T cells were detected as CD2+ cells in all groups. (E) Disease burden after 2 weeks and at termination in BM was highest in control CAR19−TCR+-treated animals (blue circles) (n = 5 [2 weeks]/n = 3 [4 weeks]). Disease was barely detected in TT-CAR19+TCR− animals (red triangles) (n = 4 [2 weeks]/n = 4 [5 weeks]) and found to be significantly reduced compared with the CAR19+TCR+ (green squares) effector group (n = 5 [2 weeks]/n = 3 [5 weeks]) at termination compared with CAR19−TCR+ 2-week values (p = 0.0357 versus p = 0.0159); error bars represent SEM. (F) Phenotypic assessment of leukemia in BM at termination uncovered the emergence of CD19−CD20+ Daudi populations in animals treated with CAR19+TCR+ cells (n = 3), whereas the leukemia detected in control animals CAR19−TCR+ (n = 3) was CD19+CD20, and the paucity of leukemia cells in TT-CAR19+TCR− animals (n = 4) precluded further characterization. (G) Representative flow cytometric data from CAR19−TCR+-treated (n = 5 [2 weeks]/n = 3 [5 weeks]), CAR19+TCR+-treated (n = 5 [2 weeks]/n = 3 [4 weeks]), or TT-CAR19+TCR−-treated (n = 4 [2 weeks)/n = 4 [5 weeks]) animals showing PD1 expression on T cells. There was markedly increased expression in CAR19−TCR+ and CAR19+TCR+ T cell-injected groups measured at 2 weeks and at termination compared with initial expression levels in cells measured in vitro (CAR19−TCR+, 20.4%; CAR19+TCR+, 20.5%; TT-CAR19+TCR−, 9.7%) before infusion into mice. CAR19+TCR+ cells showed the highest increase in PD1 at termination over the CAR19−TCR+ and TT-CAR19+TCR− groups.
By day 28, the remaining control CAR19−TCR+ animals exhibited a further 125-fold increase in tumor burden, and the mice were culled, revealing a low T cell-to-tumor ratio on flow analysis despite a significant expansion of CD45+CD2+ T cells in the final 2 weeks. The remaining treatment groups were monitored until day 34 (Figure 5A). Radiance increased in the CAR19+TCR+ group but not in the TT-CAR19+TCR− group (Figure 5C) during this period, with the bioluminescence signal appearing to localize in the bone marrow. This finding was supported by flow cytometry data showing that GFP+ Daudi cells in marrow had increased 6-fold in the CAR19+TCR+ group (*p < 0.05) (Figures 5D and 5E). Interestingly, on further analysis, we found evidence of antigen escape with clearly demarcated populations of CD20+ GFP+ Daudi cells that had lost CD19+ expression in all three animals (Figure 5F).
The TT-CAR19+TCR− group exhibited the highest levels of CAR19+ T cells at both 2 and 5 weeks and had the lowest tumor burden (Figure 5E), retaining the highest T cell:tumor ratio throughout. In contrast, the median CAR19 percentage was 34.5% (32.3–53.6) in CAR19+TCR+-treated mice at 2 weeks, and this rose to 92.9% (47.4–93.9) by 5 weeks, consistent with notable expansion of transduced populations. The intensity of CAR19 expression on flow cytometry was higher in TCR− animals than TCR+ ones, but the difference was not significant. Interestingly, TCR+ mice exhibited high levels (84.5% (55.6–89.8)) of the exhaustion marker PD1 on T cells compared with 15.1% (8.2–20.4) at 2 weeks (Figure 5G). This was also documented in non-transduced CAR19−TCR+ controls, where PD1 levels of 48.6% (37.6–49.9) at 2 weeks and 83.5% (34.9–99.1) at 4 weeks had been observed in predominantly CD4+ but also CD8+ T cells. Of note, TT-CAR19+TCR- effectors had the least exhausted phenotype with the lowest levels of PD1 expression of 6.8% (5.51–13.1) and 24.8% (16.0–50.0) at both the 2- and 5-week time points, respectively.
Discussion
There is accumulating evidence for the efficacy of T cells engineered to express CARs against leukemia antigens such as CD19 in the management of relapsed B cell malignancies.1 As well as autologous T cells, HLA-matched allogeneic T cells from hematopoietic stem cell donors have been used, and, recently, non-HLA-matched universal CAR T cells have entered clinical phase assessments.4 These cells were edited using TALENs to disrupt the TRAC locus to prevent GVHD and at the CD52 locus to confer resistance to the lymphodepleting antibody alemtuzumab. The modification process employed a multiplex approach, delivering mRNA encoding two highly specific TALEN pairs by electroporation, which conferred high-frequency allele modification but was also associated with predicted and unpredicted translocation events of unknown significance. In the case of the TRAC locus, in most T cells, allelic exclusion operates to ensure that only a single TCRαβ configuration is expressed, and, therefore, NHEJ-mediated disruption of the active allele is theoretically sufficient to disrupt cell-surface TCRαβ expression. Downstream processing using CliniMacs TCRαβ magnetic bead depletion ensures removal of residual TCRαβ+ cells and readily yields highly purified (>99%) TCRαβ− T cells. However, the shortcomings of current TALEN-based approaches include variable lentiviral transduction efficiencies between batches and, in the absence of an enrichment strategy to ensure that all cells are CAR19+, variations in total cell dosing required to achieve a particular CAR19 dose. In turn, the total T cell dose is a critical parameter that is determined, and limited by, the absolute number of residual TCRαβ cells that might be adoptively transferred as part of the total cell dose. Under existing approaches, TCRαβ− cells may be CAR19+ or CAR19−, but, by coupling gene-editing effects to CAR19 expression, the TT-CAR19 configuration yields highly purified T cells that are CAR19+TCRαβ−. This system has a number of advantages. (1) The incorporation of the CRISPR guide into the 3′ LTR mitigates interference effects and ensures intact transgene expression for highly efficient transduction and TRAC editing effects. (2) Coupling effects become fully manifest after completion of downstream processing and depletion of residual TCRαβ cells, by which stage the product is highly homogeneous CAR19+TCRαβ−. (3) Transient delivery and expression of Cas9 (as stabilized, reduced immunogenicity Cas9 mRNA) provides time-limited DNA cleavage effects and reduces the risk of immunogenicity, and, using this approach, manufacture of a single Cas9 mRNA batch can service multiple terminal vector-CRISPR RNA guide combinations, reducing costs and saving time associated with the manufacture of bespoke raw materials for different CRISPR/Cas9 targets. (4) The process is readily incorporated into an automated manufacturing platform, facilitating early clinical application.
Investigations into on- and off-target effects in TALEN-edited T cells have previously reported translocations between TRAC and CD52 target sites of up to 1%, and we previously found that around 4%–5% of cells exhibited abnormal karyotypes, with evidence of various TRAD translocations found on breakpoint FISH probe analysis.4 Similar analysis in TRAC-modified TT-CAR19+TCR− T cells did not detect any similar segregation of these FISH probes, although the sensitivity limitations of FISH mean that translocations may have occurred below the limits of detection. We used three different platforms to confirm TRAC-specific activity and the absence of off-target effects. WGS found comparable, very low frequencies of indel events across the genome, including exonic sequences, for both Cas9-treated and non-treated cells. Although there was increased detection of structural variants in the edited samples, interrogation of the highest-ranking in silico predicted off-target sites found edited and non-edited samples to have a similar frequency of changes in both WGS and higher-resolution NGS outputs. Similar findings were recorded across ten additional genes known to be sites of 14q translocations associated with T cell leukemia. There are a number of important caveats and limitations to the application of WGS for analysis of gene editing effects, including limited read depth. Digenome-seq has the capacity to detect low-frequency events (0.1%–1%), and the specificity of the TRAC guide sequence was validated with negligible off-target effects that were further interrogated by NGS and also found to be absent in Cas9-treated cells. Nuclease-mediated effects below this level, however, are difficult to confirm, given the sequencing error rates.15, 16 A single unpredicted site in RPN1 was identified by WGS and could have represented an off-target site for our TRAC-specific sgRNA, but this was discounted upon further interrogation by NGS and by Digenome-seq. This highlights a potential limitation of relying on low-depth sequencing platforms and suggests that a multi-platform approach using tools such as Digenome-seq,17 GUIDE-seq,18 or lentivirus capture19 coupled with high-resolution sequencing is paramount.
Finally, in vivo modeling revealed that TT-CAR19 T cells mediated highly effective leukemic eradication with less evidence of exhaustion compared with conventional TCR-expressing CAR19 T cells. The latter was unexpected, given that characterization of CAR19-transduced populations by flow cytometry, cytokine array profiles, and functional studies in vitro had not detected any notable differences between TCR-depleted CAR19 cells and conventional TCR+ CAR19 T cells. In human:murine chimeras bearing Daudi B cell leukemia tumor inoculations, animals dosed with TT-CAR19 T cells exhibited potent anti-leukemic effects without xenoreactive GVHD within the period of testing and reduced upregulation of the exhaustion marker PD1 compared with control groups that had retained TCR expression. This is consistent with previous murine studies20 and clinical trials of donor-derived human CAR19 T cells where TCR-mediated co-activation may drive exhaustion.21
Interestingly, flow characterization of Daudi cell surface marking in mice treated with CAR19+TCR+ T cells revealed that a notable proportion had clearly lost CD19 expression at the time of culling, and this was not evident in tumor cells recovered from control CAR19−TCR+-treated mice. This phenomenon is reminiscent of clinical reports from patients who relapsed with CD19-negative leukemia after a period of remission following CAR19 therapy, and we speculate that CD19 tumor populations acquired a survival advantage and expanded in the face of CAR19 immunity, although the absence of similar expansions in mice treated with TT-CAR19+TCR− requires further investigation with larger numbers of animals.
One advantage of T cell engineering using integrating vector systems has been their apparent resistance to possible transformational events as a result of vector integration, and to date there have been no reports of human T cell insertional mutagenesis. Even in animals, vector-mediated leukemiagenesis in T cells has rarely been encountered, and only in highly stressed artificial model systems.22 Similar resilience may be anticipated following gene editing, although loci such as the TRAC site have known translocation associations with T cell leukemia. We screened such sites by WGS, and all were found to be intact. In the absence of informative animal models, cautious deployment and careful patient monitoring will be essential to determine risks in early-phase trials. Similarly, modeling in immunodeficient mice is not representative of clinical scenarios where lymphodepleting conditioning is required to overcome host-mediated rejection of non-matched universal T cells, but accumulating experience in clinical trials is helping to determine the intensity of such regimens.
The terminal vector configuration described here utilized Streptococcus pyogenes Cas9 but is readily adapted for other similar nucleases,15, 23, 24, 25 nickases,26 deactivated Cas systems,27, 28 or cytidine deamination-linked enzymes.29 The proof-of-concept configuration described here has been adapted further to include multiple guide cassettes for multiplex modifications, including simultaneous B2m disruption to deplete MHC class I expression and PD1 disruption to promote T cell invigoration. The platform could, with certain revisions, also be used for targeted CAR insertion into the TRAC locus, as recently described using an adeno-associated virus.30 However, the first planned therapeutic applications will be more straightforward and will exploit coupling of CAR19 and TCRαβ depletion as a bridging strategy to transplantation. Thereafter, multiple applications are envisaged, where ex vivo cell manipulation requiring vector-mediated integration of transgenes encoding receptors, selection markers, or suicide genes need to be combined with therapeutic editing effects.
Materials and Methods
CRISPR-CAR Vector System
A third-generation SIN lentiviral vector described previously,31 expressing a CAR19 transgene, was subjected to cloning incorporating an HIV-1 central polypurine tract (cPPT) element, and mutated woodchuck post-transcriptional regulatory element (WPRE) for the expression of a CAR19 transgene under the control of a human PGK promoter was subjected to site-directed mutagenesis to remove BbsI, BsmbI, and SapI restriction sites using a QuickChange Lightning Kit (210518, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, USA). U6 and H1 CRISPR guide cassettes were then cloned into the ΔU3 region of the 3′ LTR using In-Fusion HD Cloning Plus (638909, Takara Bio Europe, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France). BbsI restriction sites were then incorporated between the Pol III promoter and scaffold sequences to allow for efficient guide sequence substitution. GeneART-synthesized CRISPR cassettes (Thermo Fisher Scientific, MA, USA) based on the Shalem et al.10 Streptococcus pyogenes Cas9 scaffold sequence were cloned into the ΔU3 region of the 3′ LTR. Concentrated vector preparations were produced by transient transfection of 293T cells as described previously.32, 33
Primary Human Lymphocyte Culture and Modification
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated by Ficoll-Paque density gradient and subsequently activated with TransACT reagent (130-109-104, Miltenyi Biotec, Surrey, UK). Use of white blood cells from healthy donor blood donations for the development of gene and cell adoptive immunotherapies was approved by the Research Ethics Committee (REF:14/LO/0054). Lymphocytes were cultured in TexMACS medium (130-097-196, Miltenyi Biotec) with 3% human AB serum (GEM-100-512-HI, Seralabs, Brussels, Belgium) and 100 U/mL Proleukin IL-2 (Novartis, Surrey, UK). PBMCs were transduced with lentiviral vector 24 hr after activation at an MOI of 5, and Cas9 mRNA electroporation was performed 3 days later. Lymphocytes were cultured until day 11 after activation and then cryopreserved in 90% fetal calf serum (FCS) and 10% DMSO. Scaled experiments utilized a semi-automated platform as described recently.34 Briefly, the T cell transduction (TCT) program was adapted on the CliniMACS Prodigy using tubing set TS520 (130-019-002, Miltenyi Biotec) and used cryopreserved leukapheresis harvests (Allcells, Alameda, USA) cultured in TexMACS good manufacturing practice (GMP) medium (170-076-307, Miltenyi Biotec) supplemented with 3% human AB serum (Seralabs) and 20 ng/mL MACS GMP human recombinant IL-2 (170-076-146, Miltenyi Biotec).34 Cells were activated with TransAct T cell reagent (Miltenyi Biotec), transduced 24 hr after activation at an MOI of 5, and electroporated with Cas9 mRNA on day 4.
Detection of NHEJ Events
PCR amplicons of genomic DNA were sequenced and analyzed using TIDE protocols (https://tide.nki.nl/).35 (Further details can be found in the Supplemental Materials and Methods.)
FISH Studies
Translocation events involving the TRAD locus were investigated using a dual-color, break-apart FISH probe (Cytocell TCRAD LPH 047-S; 14q11, red/green fusion) to interrogate interphase nuclei. A normal signal pattern comprises 2 fusion signals, and TRAD rearrangements exhibit segregated single red/green markers.
In Vitro Cytotoxicity
The cytotoxic function of CAR19−TCR+, CAR19+TCR+, and TT-CAR19+TCR− T cells was assessed by co-culture with 51Cr-loaded CD19+ or CD19− SupT1 target cells at increasing effector-to-target (E:T) ratios in a 96-well format for 4 hr at 37°C. Release of 51Cr was quantified using a microplate scintillation counter, and specific cytotoxicity was calculated.
NGS
On-target and potential off-target sites were amplified using Phusion polymerase (New England Biolabs), and the resulting PCR amplicons were amplified again using TruSeq HT Dual Index primers to make a library. Libraries were then subjected to paired-end sequencing using MiniSeq (Illumina).
Digenome-Seq
To induce Cas9-mediated in vitro cleavage of genomic DNA, 100 nM Cas9 protein and 300 nM TRAC-targeting sgRNA were incubated with 10 μg genomic DNA in a reaction buffer of 500 μL (100 mM NaCl, 50 mM Tris-HCl, 10 mM MgCl2, and 100 μg/mL BSA [pH 7.9]) at 37°C for 8 hr. Digested DNA was incubated with 50 μg/mL RNase A (QIAGEN) at 37°C for 30 min to remove sgRNA and purified again with a DNeasy Tissue Kit (QIAGEN). Digested genomic DNA was fragmented with a Covaris system (Life Technologies) and ligated with adapters to produce libraries that were subjected to WGS using a HiSeq X Ten Sequencer (Illumina) at Macrogen. Cas9-mediated in vitro cleavage of genomic DNA was performed, and DNA cleavage scores were calculated using a scoring system described previously.17, 36
WGS
Genomic DNA was extracted from CAR19+TCR+ and TT-CAR19+TCR− cells using the DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit (QIAGEN). Approximately 1.5 μg of genomic DNA was analyzed at Applied Biological Materials Inc. (Richmond, BC, Canada), by 30× WGS using the MiSeq platform. Overall alignment rates were >99.9% and correct pairing ≫98.3%. GATK and DELLY were used to identify single nucleotide variance, indels, and other structural differences. Targeted assessment of the TRAC locus and 49 predicted possible off-target sites was undertaken as well as screening of ten known gene sites where translocations of 14q have known leukemic associations.
In Vivo Anti-tumor Activity
NSG mice were inoculated intravenously (i.v.) with 5 × 105 CD19+ Daudi tumor cells by tail vein injection on day 0. The tumor cells had been stably transduced to express both EGFP and luciferase. Tumor engraftment was confirmed by in vivo imaging of bioluminescence using an IVIS Lumina III In Vivo Imaging System (PerkinElmer, MA, USA, live image version 4.5.18147) on day 3. Animals were injected on day 4 with either PBS (n = 3), 5 × 106 untransduced CAR19−TCR+ T cells (n = 8), 8 × 106 CAR19+TCR+ T cells (n = 8), or 5 × 106 TT-CAR19+TCR− T cells (n = 8). Analysis of tumor clearance was performed by serial bioluminescence imaging, and processing of bone marrow for the monitoring of tumor progression versus clearance was carried out on days 7, 10, 14, 18, 21, 28, and 35. Bone marrow samples were processed by red blood cell lysis followed by staining for flow cytometry. All animal studies were approved by the University College London Biological Services Ethical Review Committee and licensed under the Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986 (Home Office, London, United Kingdom). (Further details can be found in the Supplemental Materials and Methods.)
Statistics
A two-tailed Mann-Whitney U test was used for non-parametric comparison of grouped data, and values are presented as mean percentages of three or more samples with SEM or SD or as a median with the 25th and 75th percentiles (50% central range) stated. Linear regression was used for the comparison of serial measurements, taking each Y value as an individual point. All statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism software version 5.01.
Author Contributions
C.G., R.P., and W.Q. designed the project and wrote the manuscript. C.G. and R.P. developed the vector and performed in vitro and in vivo experiments and data analysis. L.N. managed the scale-up manufacture and assisted with the CBA assay. A.E. performed the degranulation assay. A.P. carried out analysis of on- and off-target sites by NGS. D.L. carried out the FISH analysis. A.D., N.H.-K., and A.A. undertook the WGS analysis for the characterization of predicted of on- and off-target effects. D.K. and J.-S.K. performed off-target analysis by NGS, WGS, and Digenome-seq.
Conflicts of Interest
A.D., N.H-K., and A.A. hold interests/are employees of Desktop Genetics. W.Q. holds interests unrelated to this project in Autolus Ltd. and Orchard Therapeutics. W.Q. receives unrelated research funding from Cellectis, Servier, Miltenyi, and Bellicum.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institute of Health Research (NIHR) (RP-2014-05-007), NIHR Blood and Transplant Research Unit (BTRU) (BTRU-2014-10074), Great Ormond Street Biomedical Research Centre (IS-BRC-1215-20012), and Children with Cancer (2014/171). The views expressed are those of the author(s) and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR, or the Department of Health. We would like to extend our gratitude to Dr. Carolina B. Ferreira for her assistance and expertise in RT-PCR and WB assays.
Footnotes
Supplemental Information includes Supplemental Materials and Methods, two figures, and two tables and can be found with this article online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.02.025.
Supplemental Information
References
- 1.Rivière I., Sadelain M. Chimeric Antigen Receptors: A Cell and Gene Therapy Perspective. Mol. Ther. 2017;25:1117–1124. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.03.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Torikai H., Reik A., Liu P.Q., Zhou Y., Zhang L., Maiti S., Huls H., Miller J.C., Kebriaei P., Rabinovich B. A foundation for universal T-cell based immunotherapy: T cells engineered to express a CD19-specific chimeric-antigen-receptor and eliminate expression of endogenous TCR. Blood. 2012;119:5697–5705. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-01-405365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Provasi E., Genovese P., Lombardo A., Magnani Z., Liu P.Q., Reik A., Chu V., Paschon D.E., Zhang L., Kuball J. Editing T cell specificity towards leukemia by zinc finger nucleases and lentiviral gene transfer. Nat. Med. 2012;18:807–815. doi: 10.1038/nm.2700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Qasim W., Zhan H., Samarasinghe S., Adams S., Amrolia P., Stafford S., Butler K., Rivat C., Wright G., Somana K. Molecular remission of infant B-ALL after infusion of universal TALEN gene-edited CAR T cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017;9 doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaj2013. eaaj2013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Poirot L., Philip B., Schiffer-Mannioui C., Le Clerre D., Chion-Sotinel I., Derniame S., Potrel P., Bas C., Lemaire L., Galetto R. Multiplex Genome-Edited T-cell Manufacturing Platform for “Off-the-Shelf” Adoptive T-cell Immunotherapies. Cancer Res. 2015;75:3853–3864. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-3321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bertaina A., Merli P., Rutella S., Pagliara D., Bernardo M.E., Masetti R., Pende D., Falco M., Handgretinger R., Moretta F. HLA-haploidentical stem cell transplantation after removal of αβ+ T and B cells in children with nonmalignant disorders. Blood. 2014;124:822–826. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-03-563817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Osborn M.J., Webber B.R., Knipping F., Lonetree C.L., Tennis N., DeFeo A.P., McElroy A.N., Starker C.G., Lee C., Merkel S. Evaluation of TCR Gene Editing Achieved by TALENs, CRISPR/Cas9, and megaTAL Nucleases. Mol. Ther. 2016;24:570–581. doi: 10.1038/mt.2015.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ren J., Zhang X., Liu X., Fang C., Jiang S., June C.H., Zhao Y. A versatile system for rapid multiplex genome-edited CAR T cell generation. Oncotarget. 2017;8:17002–17011. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ren J., Liu X., Fang C., Jiang S., June C.H., Zhao Y. Multiplex Genome Editing to Generate Universal CAR T Cells Resistant to PD1 Inhibition. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016;23:2255–2266. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Shalem O., Sanjana N.E., Hartenian E., Shi X., Scott D.A., Mikkelson T., Heckl D., Ebert B.L., Root D.E., Doench J.G., Zhang F. Genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screening in human cells. Science. 2014;343:84–87. doi: 10.1126/science.1247005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Adam M.A., Osborne W.R., Miller A.D. R-region cDNA inserts in retroviral vectors are compatible with virus replication and high-level protein synthesis from the insert. Hum. Gene Ther. 1995;6:1169–1176. doi: 10.1089/hum.1995.6.9-1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Szulc J., Wiznerowicz M., Sauvain M.O., Trono D., Aebischer P. A versatile tool for conditional gene expression and knockdown. Nat. Methods. 2006;3:109–116. doi: 10.1038/nmeth846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Curtin J.A., Dane A.P., Swanson A., Alexander I.E., Ginn S.L. Bidirectional promoter interference between two widely used internal heterologous promoters in a late-generation lentiviral construct. Gene Ther. 2008;15:384–390. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3303105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hsu P.D., Lander E.S., Zhang F. Development and applications of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome engineering. Cell. 2014;157:1262–1278. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.05.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kleinstiver B.P., Pattanayak V., Prew M.S., Tsai S.Q., Nguyen N.T., Zheng Z., Joung J.K. High-fidelity CRISPR-Cas9 nucleases with no detectable genome-wide off-target effects. Nature. 2016;529:490–495. doi: 10.1038/nature16526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tycko J., Myer V.E., Hsu P.D. Methods for Optimizing CRISPR-Cas9 Genome Editing Specificity. Mol. Cell. 2016;63:355–370. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.07.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kim D., Bae S., Park J., Kim E., Kim S., Yu H.R., Hwang J., Kim J.I., Kim J.S. Digenome-seq: genome-wide profiling of CRISPR-Cas9 off-target effects in human cells. Nat. Methods. 2015;12:237–243. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tsai S.Q., Zheng Z., Nguyen N.T., Liebers M., Topkar V.V., Thapar V., Wyvekens N., Khayter C., Iafrate A.J., Le L.P. GUIDE-seq enables genome-wide profiling of off-target cleavage by CRISPR-Cas nucleases. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015;33:187–197. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Knipping F., Osborn M.J., Petri K., Tolar J., Glimm H., von Kalle C., Schmidt M., Gabriel R. Genome-wide Specificity of Highly Efficient TALENs and CRISPR/Cas9 for T Cell Receptor Modification. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2017;4:213–224. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2017.01.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jacoby E., Yang Y., Qin H., Chien C.D., Kochenderfer J.N., Fry T.J. Murine allogeneic CD19 CAR T cells harbor potent antileukemic activity but have the potential to mediate lethal GVHD. Blood. 2016;127:1361–1370. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-08-664250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ghosh A., Smith M., James S.E., Davila M.L., Velardi E., Argyropoulos K.V., Gunset G., Perna F., Kreines F.M., Levy E.R. Donor CD19 CAR T cells exert potent graft-versus-lymphoma activity with diminished graft-versus-host activity. Nat. Med. 2017;23:242–249. doi: 10.1038/nm.4258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Newrzela S., Cornils K., Li Z., Baum C., Brugman M.H., Hartmann M., Meyer J., Hartmann S., Hansmann M.L., Fehse B., von Laer D. Resistance of mature T cells to oncogene transformation. Blood. 2008;112:2278–2286. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-12-128751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ran F.A., Cong L., Yan W.X., Scott D.A., Gootenberg J.S., Kriz A.J., Zetsche B., Shalem O., Wu X., Makarova K.S. In vivo genome editing using Staphylococcus aureus Cas9. Nature. 2015;520:186–191. doi: 10.1038/nature14299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zetsche B., Gootenberg J.S., Abudayyeh O.O., Slaymaker I.M., Makarova K.S., Essletzbichler P., Volz S.E., Joung J., van der Oost J., Regev A. Cpf1 is a single RNA-guided endonuclease of a class 2 CRISPR-Cas system. Cell. 2015;163:759–771. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.09.038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Fonfara I., Richter H., Bratovič M., Le Rhun A., Charpentier E. The CRISPR-associated DNA-cleaving enzyme Cpf1 also processes precursor CRISPR RNA. Nature. 2016;532:517–521. doi: 10.1038/nature17945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ran F.A., Hsu P.D., Lin C.Y., Gootenberg J.S., Konermann S., Trevino A.E., Scott D.A., Inoue A., Matoba S., Zhang Y., Zhang F. Double nicking by RNA-guided CRISPR Cas9 for enhanced genome editing specificity. Cell. 2013;154:1380–1389. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.08.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Maeder M.L., Linder S.J., Cascio V.M., Fu Y., Ho Q.H., Joung J.K. CRISPR RNA-guided activation of endogenous human genes. Nat. Methods. 2013;10:977–979. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Perez-Pinera P., Kocak D.D., Vockley C.M., Adler A.F., Kabadi A.M., Polstein L.R., Thakore P.I., Glass K.A., Ousterout D.G., Leong K.W. RNA-guided gene activation by CRISPR-Cas9-based transcription factors. Nat. Methods. 2013;10:973–976. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Komor A.C., Kim Y.B., Packer M.S., Zuris J.A., Liu D.R. Programmable editing of a target base in genomic DNA without double-stranded DNA cleavage. Nature. 2016;533:420–424. doi: 10.1038/nature17946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Eyquem J., Mansilla-Soto J., Giavridis T., van der Stegen S.J., Hamieh M., Cunanan K.M., Odak A., Gönen M., Sadelain M. Targeting a CAR to the TRAC locus with CRISPR/Cas9 enhances tumour rejection. Nature. 2017;543:113–117. doi: 10.1038/nature21405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Dull T., Zufferey R., Kelly M., Mandel R.J., Nguyen M., Trono D., Naldini L. A third-generation lentivirus vector with a conditional packaging system. J. Virol. 1998;72:8463–8471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.72.11.8463-8471.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Demaison C., Parsley K., Brouns G., Scherr M., Battmer K., Kinnon C., Grez M., Thrasher A.J. High-level transduction and gene expression in hematopoietic repopulating cells using a human immunodeficiency [correction of immunodeficiency] virus type 1-based lentiviral vector containing an internal spleen focus forming virus promoter. Hum. Gene Ther. 2002;13:803–813. doi: 10.1089/10430340252898984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Qasim W., Mackey T., Sinclair J., Chatziandreou I., Kinnon C., Thrasher A.J., Gaspar H.B. Lentiviral vectors for T-cell suicide gene therapy: preservation of T-cell effector function after cytokine-mediated transduction. Mol. Ther. 2007;15:355–360. doi: 10.1038/sj.mt.6300042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Mock U., Nickolay L., Philip B., Cheung G.W., Zhan H., Johnston I.C., Kaiser A.D., Peggs K., Pule M., Thrasher A.J., Qasim W. Automated manufacturing of chimeric antigen receptor T cells for adoptive immunotherapy using CliniMACS prodigy. Cytotherapy. 2016;18:1002–1011. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2016.05.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Brinkman E.K., Chen T., Amendola M., van Steensel B. Easy quantitative assessment of genome editing by sequence trace decomposition. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:e168. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kim D., Kim S., Kim S., Park J., Kim J.S. Genome-wide target specificities of CRISPR-Cas9 nucleases revealed by multiplex Digenome-seq. Genome Res. 2016;26:406–415. doi: 10.1101/gr.199588.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.