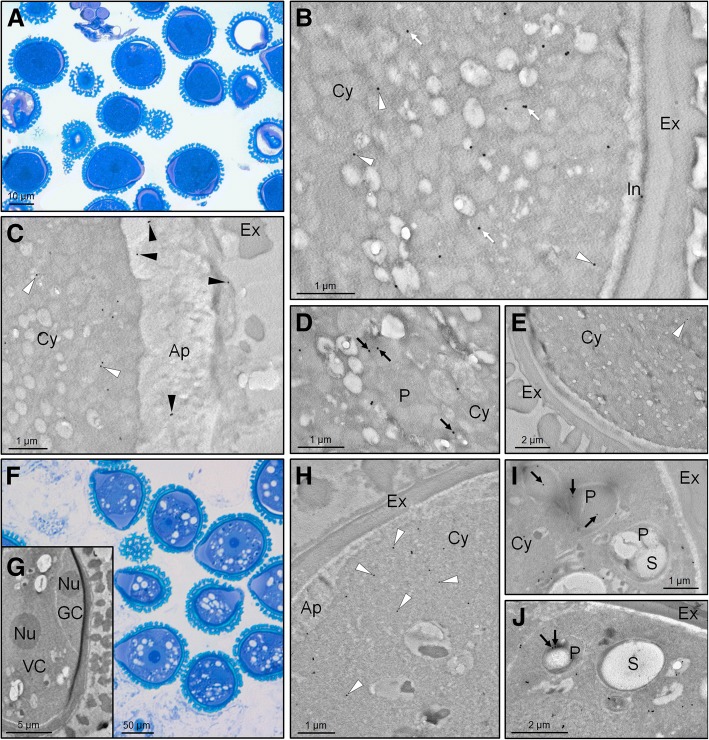
Fig. 6.
Transmission electron microscopy immunolocalization of SOD enzymes in olive developing pollen grains. a Light microscopy methylene blue-stained section of olive mature pollen grains (free pollen grains released from anthers). b-d Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) immunolocalization of Cu,Zn-SODs on sections of olive mature pollen grains using an anti-olive Cu,Zn-SOD Ab. e Negative control by omitting the primary antibody. f-g Light microscopy methylene blue-stained (f) and TEM (g) sections of olive young pollen grains (prior to anther dehiscence). h-j TEM immunolocalization of Cu,Zn-SODs on sections of olive young pollen using the same Ab. Black and white arrowheads indicate exine/aperture and cytosolic locations, respectively. Black arrows show the plastidial SOD, while white arrows point out undetermined-organelle locations of the enzyme. Note that plastids in the young pollen grain may display different degrees of differentiation and presence/absence of starch depending on section orientation. Abbreviations = Ap, aperture; Cy, cytoplasm; Ex, exine; GC, generative cell; I, intine; P, plastid; S, starch; Nu, nucleolus; VC, vegetative cell