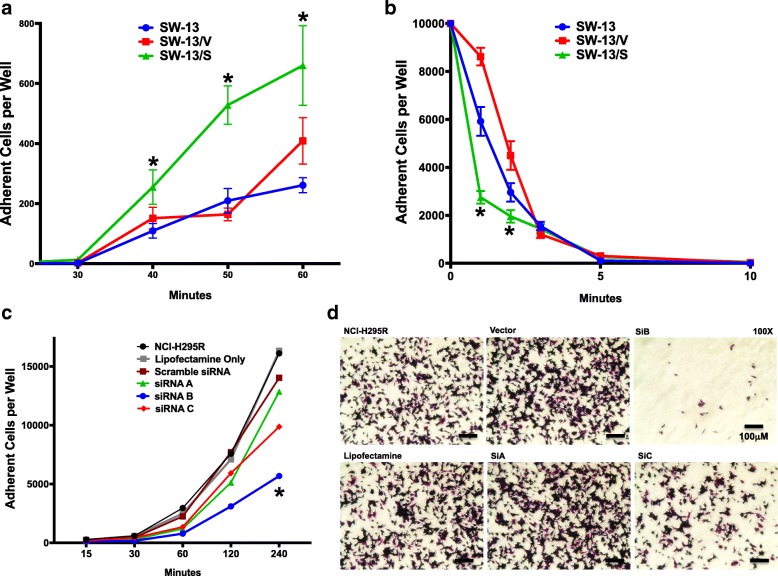
Fig. 5.
SW-13 cell adhesion and detachment kinetics analysis. a Ten thousand cells per well of SW-13, SW-13/V, and SW-13/S were incubated in complete medium (CM) at various time points to allow for cell adherence. After designated time point, cells were washed and attached cells were counted. SW-13/S cells adhered more readily (*, p < 0.05, two-way ANOVA). Horizontal bar, mean; Error bars, standard error of mean. Adhesion assay was performed in 2 independent experiments using 4 wells per each cell type analyzed. b Ten thousand cells per well of SW-13, SW-13/V, and SW-13/S were incubated in CM overnight. The following day cells were detached at designated time points with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid tetrasodium salt dehydrate (Sigma-Aldrich). The cells that remained attached were counted. SW-13/S cells detached more readily (*, p < 0.05, two-way ANOVA). Horizontal bar, mean; Error bars, standard error of mean. Detachment assay was performed in 2 independent experiments using 4 wells per each cell type analyzed. c Two hundred fifty thousands cells per well of NCI-H295R undergoing SLC12A7 RNAi gene silencing (siRNA A, B, C) were incubated in CM for various time points to allow for cell adherence. Parental cells, cells mocked transfected, and cells transfected with scrambled siRNA were used as controls. After each time point, cells were washed and counted. NCI-H295 cells undergoing RNAi gene silencing adhered less readily (*, p < 0.05, two-way ANOVA). Adhesion assay was performed in 2 independent experiments using 3 wells per each cell type analyzed. d Photomicrographs of NCI-H295R cells remaining attached after 2 h, fixed, stained with 0.5% crystal violet, and observed under 200X magnification