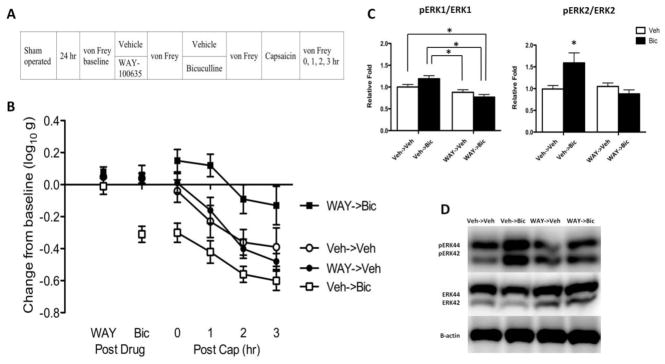
Fig. 1.
WAY-100635 switches how bicuculline affects nociceptive sensitization in intact rats. (A) The experimental design is illustrated at the top of the figure. A day after surgery, rats received WAY-100635 (WAY; black) or vehicle (Veh; white). Fifteen min later, rats received bicuculline (Bic; squares) or its vehicle (Veh; circles). Another fifteen min later, capsaicin was applied to the dorsal surface of one hind paw. (B) Mechanical reactivity after drug and capsaicin treatment. The y-axis depicts the linearized mechanical scores [log 10 (10,000g)] as a change from baseline after WAY-100635 and bicuculline treatment (Post Drug), and 0, 1, 2, 3 hr after capsaicin treatment (Post Cap). (C) Ratio of pERK1 to ERK1 (44 kDa) and pERK2 to ERK2 (42 kDa) expression in subjects that had previously received vehicle or WAY-100635. (D) Representative Western blots for ERK1/2 and pERK1/2 expression. Error bars depict ± SEM