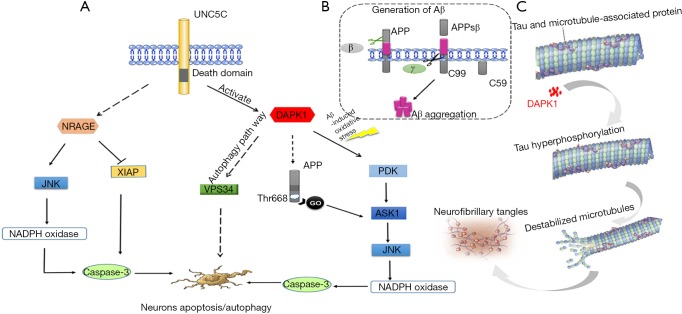
Figure 2.
Summary of the speculative roles of UNC5C in AD pathogenesis. (A) Aberrant UNC5C would activate the expression of DAPK1 then activated DAPK1 would sequential activate its downstream of PKD, ASK1, JNK, NADPH oxidase, caspases and ultimately led to a common caspases-dependent neuronal apoptosis. DAPK1-induced Vps34 pathways also may be a possible pathway to trigger neuronal autophagy. In addition, activated DAPK1 could phosphorylate APP at Thr668, which would lead to neuronal death by Aβ-independent GO protein pathway. On the other hand, the UNC5C also may be possible to be related to NRAGE-associated pathway. The aberrant NRAGE may activate its downstream of JNK, which would ultimately lead to caspases-dependent neuronal death. What’s more, the NRAGE may also degrade the caspase inhibitor XIAP, which would trigger the increase of caspases and result in promoting to neuronal apoptosis; (B) Aβ is generated via cleaving fragment of APP via β-secretase and γ-secretase. Firstly, APP is cleaved by β-secretase at the corresponding site and then releases APPsβ ectodomain. Secondly, the remaining carboxy-terminal fragment is cleaved by γ-secretase and then Aβ is released; (C) aberrant UNC5C over activate DAPK1, overexpression of DAPK1 will lead to tau protein hyper phosphorylation and ultimately promote to the form of NFT. AD, Alzheimer’s disease; DAPK1, death-associated protein kinase 1; PKD, protein kinase D; ASK1, apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1; APP, amyloid-β protein precursor; Aβ, β-amyloid protein; NRAGE, neurotrophin receptor p75-interacting melanoma-associated antigen homolog; XIAP, X-chromosome-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein; NFT, neurofibrillary tangle.