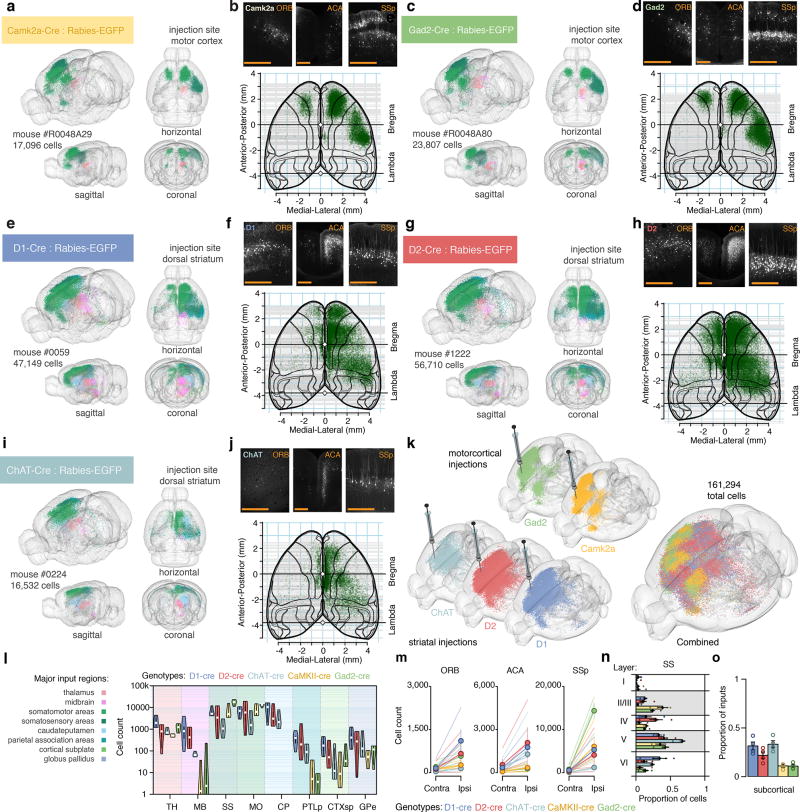
Figure 6. Retrograde monosynaptic tracing of corticostriatal networks.
(a) Reconstruction of inputs to Camk2a neurons in motor cortex by targeted injection of glycoprotein-deleted EGFP expressing EnvA pseudotyped rabies virus, SADΔG-EGFP(EnvA). EGFP labeled neurons are color-coded based on anatomical location, see (l). (b) Cortical input to Camk2a neurons in motor cortex in orbital cortex (ORB), anterior cingulate area (ACA) and primary somatosensory area, SSp. Bottom: cortical overview of inputs from cortical cells roughly above −2.25 mm dorsoventral from the midline cortical surface.(c,d) Same as (a,b) but for Gad2 neurons in motor cortex. (e, f) D1+ medium spiny neurons in dorsal striatum. (g, h) D2+ medium spiny neurons in dorsal striatum. (i, j) Cholinergic interneurons in dorsal striatum.(k) llustration of rabies-EGFP labeling in individual brains (from five different transgenic Cre-lines) used for cell-type specific input comparisons. The brain in the very front is a composite where all neurons are combined (n = 161,294 neurons across five mice). (l) Violin plot of monosynaptic inputs from major input regions (n = 4 mice for each genotype). (m) Laterality of cortical inputs in specific regions (ORB, ACA, SSp). (n) Layer-specificity of monosynaptic inputs from SSp. Colors as in (l). (o) Proportion of inputs from subcortical regions. Circles show individual mice. Colors as in (l). Error bars: +/− one standard error of measurement. Scale bars: 500 µm.