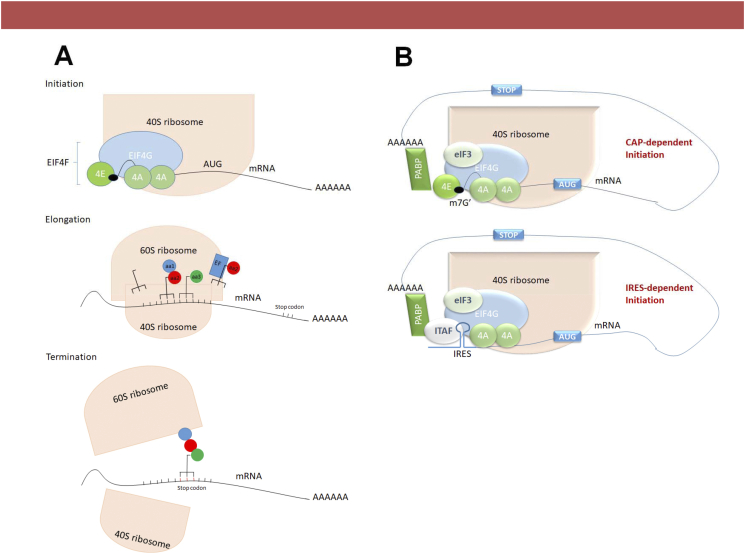
Figure 1.
(A) Steps of eukaryotic protein translation. At initiation, the eukaryotic translation initiation complex eIF4F, bound to the small ribosomal subunit 40S scans the messenger RNA (mRNA) for the start codon, when then the big ribosomal 60S subunit binds the complex to initiate translation. At Elongation, amynoacylated transfer RNAs (tRNA) bring together amino acids to be bound together by eukaryotic elongation factors (eEFs) through peptide bonds forming a chain. In the termination phase, the stop codon is read by the complex, releasing the large ribosomal subunit and terminating synthesis. (B) Protein translation initiation mechanisms. Cap-dependent initiation takes place with binding of the eIF4E to the m7G 5′ PCa of the mRNA and bringing together all proteins to form the eIF4F protein translation initiation complex. Alternatively, Cap-independent translation, or translation initiation by internal ribosomal entry site (IRES) does not need the mRNA PCa binding to eIF4E, utilizing a group of proteins named IRES trans-activating factors (ITAFs).