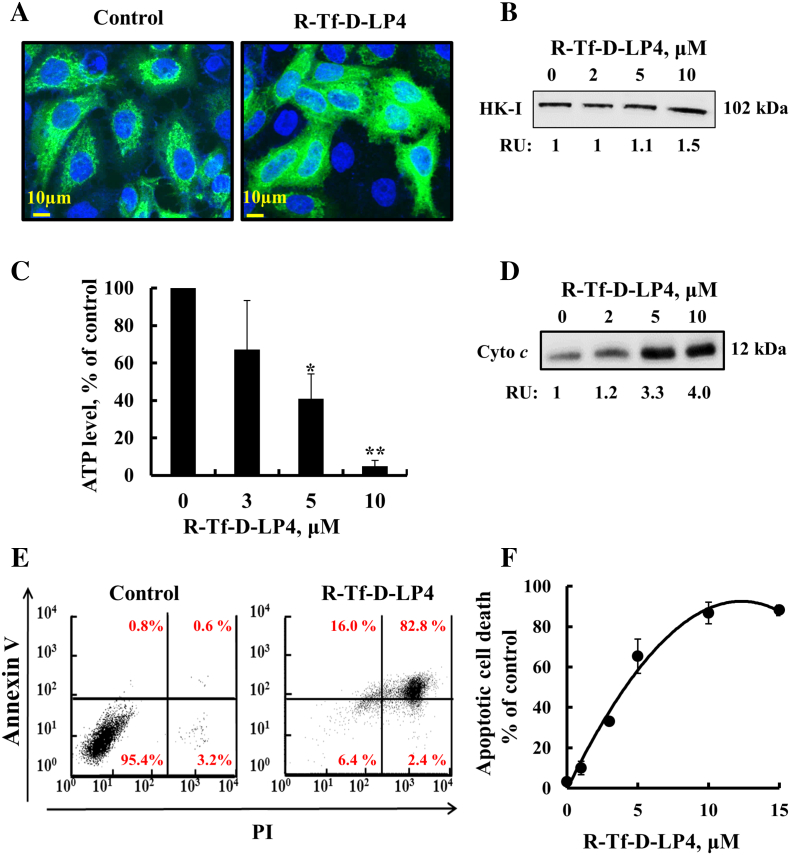
Figure 2.
R-Tf-D-LP4 induces cell death: mode of action.
R-Tf-D-LP4 induces detachment of HK-I-GFP (A) and endogenous HK-I in HepG2 cells analyzed by immunoblotting of cytosolic fraction and presented as relative units (B), as described in Materials and Methods. (C) R-Tf-D-LP4 reduces cellular ATP levels, assayed as described in Materials and Methods. Results show means ±SE (n = 3) (*P ≤ .05, **P ≤ .01). (D) R-Tf-D-LP4–induced Cyto c release from mitochondria was analyzed by immunoblotting cytosolic fraction as described in Materials and Methods. (E, F) R-Tf-D-LP4–induced apoptosis as analyzed by Annexin V-FITC and PI staining and flow cytometry. Representative FACS analysis of control and R-Tf-D-LP4 (5 μM)–treated HepG2 cells (E). Apoptosis as a function of R-Tf-D-LP4 concentration. Results show means ±SE (n = 3).