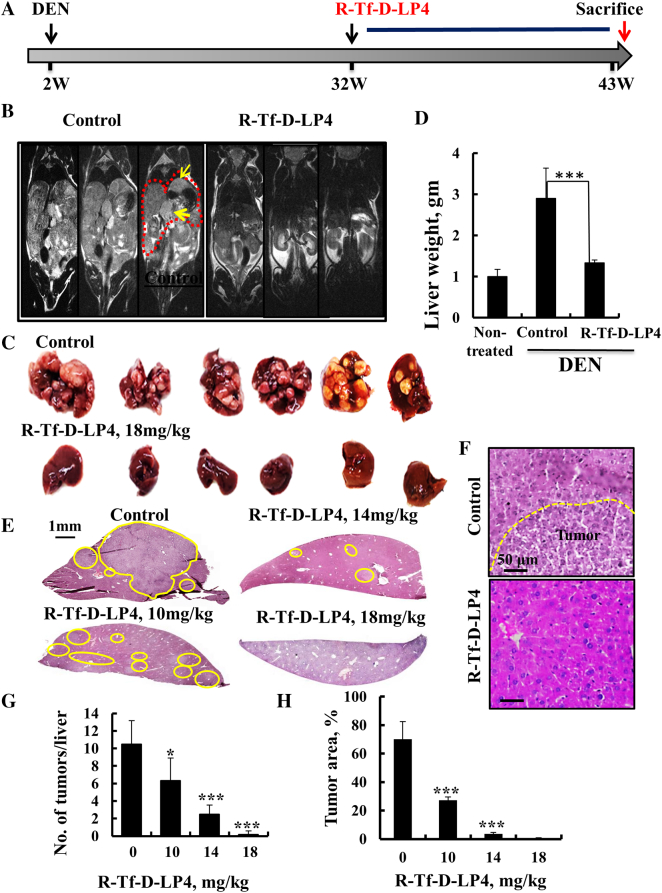
Figure 3.
VDAC1-based peptide R-Tf-D-LP4 inhibits tumor growth in a DEN-induced mouse liver cancer model. (A) A schematic presentation of DEN-induced liver cancer development and treatment schedule. (B) MRI of the abdomens of 42-week-old mice treated i.v. with HBSS or R-Tf-D-LP4 (18 mg/kg, n = 30) for 10 weeks as described in Materials and Methods. (C, D) Dissected (C) and weighed (D) livers from DEN-treated, peptide-untreated, and R-Tf-D-LP4–treated DEN-mice. (E) H&E staining of liver sections from untreated and R-Tf-D-LP4–treated mice [0, 10, 14 mg/kg (n = 8) and 18 mg/kg, n = 30]. (F) A higher magnification of H&E staining of liver sections from untreated (with the tumor indicated) and R-Tf-D-LP4–treated mice (18 mg/kg) is shown. The numbers of tumors per liver (G) and tumor areas (H) were measured with a Pannoramic MIDI, 3DHISTECH microscope (Pannoramic viewer, 3DHISTECH). (*P ≤ .05, ***P ≤ .001).