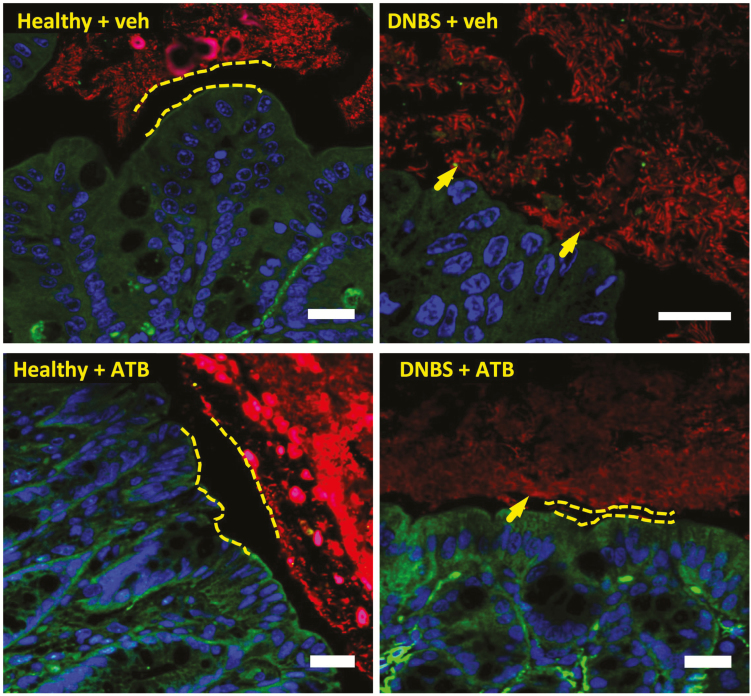
FIGURE 5.
ATB-429 restores normal gut microbiota biofilm localization. C57Bl/6 mice were given DNBS intracolonically to induce colitis, treated orally with ATB-429 (50 mg/kg, twice daily), and killed after 5 days (n = 8 per group). Intestinal microbiota biofilms were stained by fluorescent in situ hybridization (Eubacteria probe, in red), host nuclei were labeled with To-pro-3 (in blue), and the epithelial host cytoskeleton was stained with an F-actin-FITC antibody (in green). In animals with colitis, bacteria invaded the mucus layer and adhered to epithelium (arrows), whereas in healthy and in ATB-429-treated mice, the microbiota remained separated from the epithelial surface by a normal mucus layer. Scale bars represent 20 µm, dashed lines represent the sterile mucus layer.