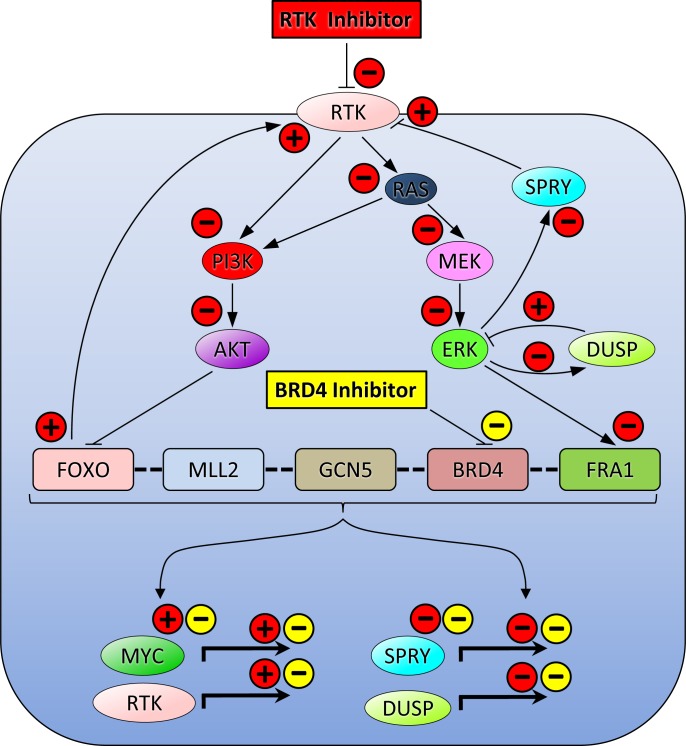
Figure 6. A model summarizing the mechanisms of cooperation between RTK signaling and BRD4-controlled epigenetic regulation of oncogene expression and activation reveals nodes for combined targeting in order to disable compensatory bypass routes.
RTKs are upstream activators of PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK. AKT is known to block the interaction of FOXO transcription factors with the histone methyltransferase MLL2, the histone acetyltransferase GCN5 and the chromatin reader BRD4. The MAPK ERK, on the other hand, activates the terminal transcription factor FRA1, which–just like BRD4–binds to the MYC super-enhancer. Thus, all these transcription regulators cooperate with BRD4 in order to control the expression of oncogenes such as MYC and RTKs. Consequently, an RTK inhibitor (red rectangle), e.g. ponatinib, abrogates PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK/FRA1 (red minus signs) neutralizing FOXO-, SPRY-, and DUSP-mediated negative feedback regulation of RTK and ERK and enabling transcription of MYC and RTKs (red plus signs), while abrogating the transcription of SPRY and DUSP, two negative modulators of RTK and ERK, respectively (red minus signs). Importantly, these feedback loops can be impeded by concurrent exposure to BRD4 inhibitors such as JQ1 or dBET1 (yellow rectangle), which diminish transcription of MYC and RTKs, and of RTK- and ERK-antagonistic genes such as SPRY and DUSP (yellow minus signs). Pointed or blunt arrows indicate stimulation or inhibition, respectively. Bold dashed lines signify assembly of the transcriptional regulator complex (bracket). Bold right-angle arrows depict gene transcription. Abbreviations: BRD4, bromodomain-containing protein 4; DUSP, dual specificity protein phosphatase; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FOXO, forkhead box protein O; FRA1, fos-related antigen 1; GCN5, general control of amino acid synthesis protein 5; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MEK, dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; MLL2, mixed-lineage leukemia protein 2; MYC, myelocytomatosis oncogene; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase; RAS, rat sarcoma oncogene; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase; SPRY, sprouty.