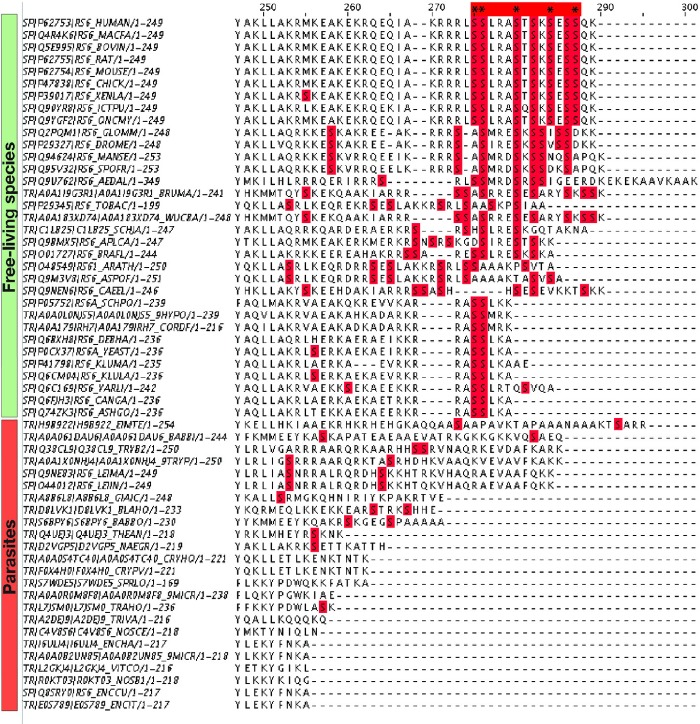
Fig. 5.
Variations in protein eS6 as a possible adaptation to specific lifestyles. The figure shows a multiple sequence alignment for eukaryotic ribosomal protein eS6 (C-terminal fragment). The C-terminal eS6 segment endows ribosomes with sensitivity to nutrients: it harbors serine residues (highlighted by asterisks) that are phosphorylated in response to hormones and nutrient availability to readjust the overall rate of protein synthesis in a eukaryotic cell. The figure shows that the phosphorylation sites remain conserved in free-living species but are degenerated in parasites, suggesting the lack of a nutrient sensor within parasitic ribosomes.