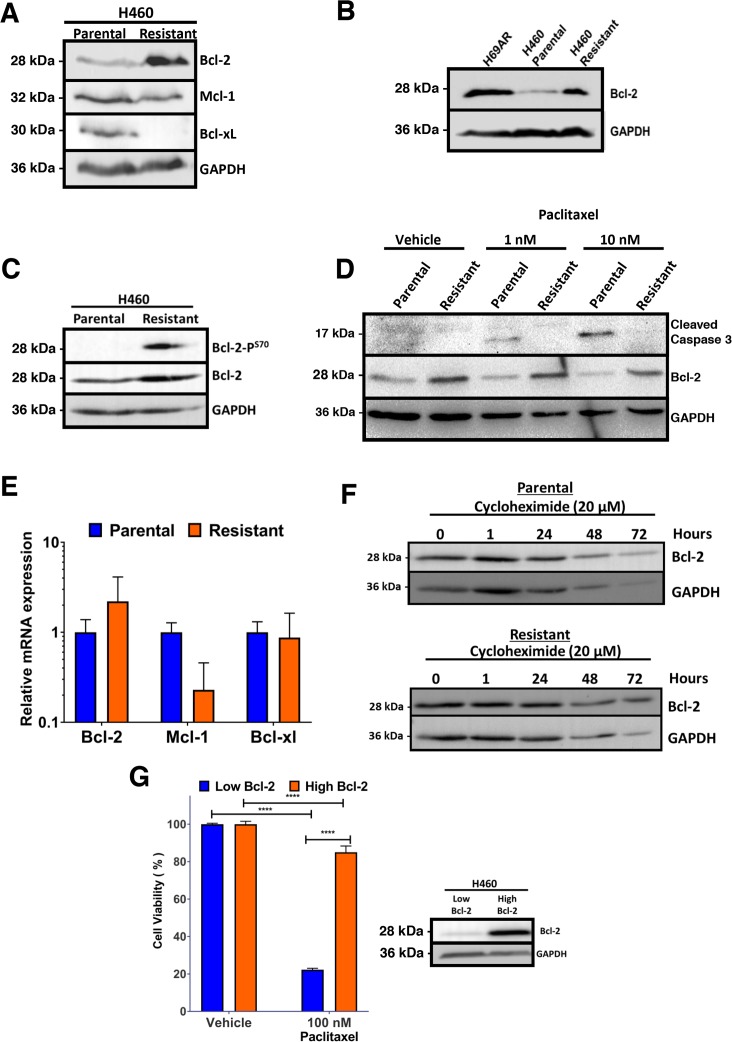
Figure 2. Paclitaxel resistant H460 cells express elevated levels of Bcl-2.
(A) Increased Bcl-2 expression in Paclitaxel resistant H460 cells. Western blot analysis of H460 parental and derived paclitaxel resistant cells. (B) High Bcl-2 expression in multidrug resistant H69AR and paclitaxel resistant H460 cells compared to parental H460 cells. Western blot analysis of multidrug resistant H69AR and H460 parental and paclitaxel resistant cells probed with indicated antibodies. (C) Increased phosphorylation of Bcl-2 at serine 70 in H460 paclitaxel resistant cells. Western blot analysis of H460 parental and paclitaxel resistant cells blotted with indicated antibodies. (D) Correlation of high Bcl-2 and increased resistance to paclitaxel. Western blot analysis of H460 parental and paclitaxel resistant cells treated with paclitaxel for 48 hours and probed with indicated antibodies. (E) Analysis of Bcl-2, Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL mRNA levels in parental and resistant H460 cells using quantitative real-time PCR. (F) Bcl-2 protein stability is not altered in parental and paclitaxel resistant cells. The level of Bcl-2 was detected by Western blot and GAPDH was used as a loading control. (G) Bcl-2 expression alone confers resistance to paclitaxel. Flow cytometry-based analysis of viability in H460 parental cells expressing Bcl-2 or control vector, after treatment with 100 nM paclitaxel for 48 hours; right panel: Western blot analysis of transfected cells show increased Bcl-2 expression. Results are the mean±s.d. Two-way ANOVA, with Sidaks multiple comparison post-test, **** = P<0.0001.