Figure 1.
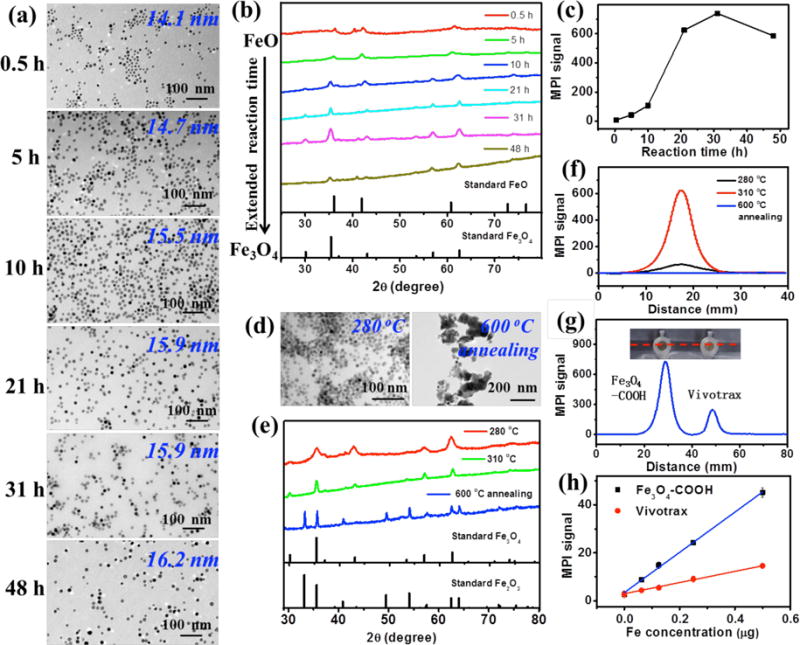
(a–c) Characterization of iron oxide nanocrystals synthesized by thermal decomposition of an iron-oleate complex at 310 °C with various reaction times (e.g. 0.5, 5, 10, 21, 31, 48 h). (a) TEM images of iron oxide nanoparticles synthesized at 310 °C. (b) Powder XRD patterns of iron oxide nanoparticles synthesized at 310 °C. (c) MPI peak signals of PSMA-modified iron oxide nanoparticles synthesized at 310 °C with the same amount of Fe (8 μg) in 200 μL H2O. (d–f) Characterization of iron oxide nanocrystals synthesized by thermal decomposition of an iron-oleate complex at 21 h with 280 °C and 310 °C, and iron oxide nanocrystals (prepared at 310 °C / 21 h) annealed at 600 °C for 2 h in air atmosphere. (d) TEM images of as-prepared iron oxide nanoparticles. (e) Powder XRD patterns of as-prepared iron oxide nanoparticles. (f) Linear scanning MPI spectra of as-prepared iron oxide nanoparticles with the same amount of Fe (8 μg) in 200 μL H2O. (g) Photograph of PCR tube containing 200 μL of Fe3O4-COOH (prepared at 310 °C / 31 h) and Vivotrax with the same amount of Fe (8 μg), and corresponding linear scanning MPI spectra. (h) Plot of the MPI signals of Fe3O4-COOH (prepared at 310 °C / 31 h) and Vivotrax versus the amount of Fe in 200 μL H2O.
