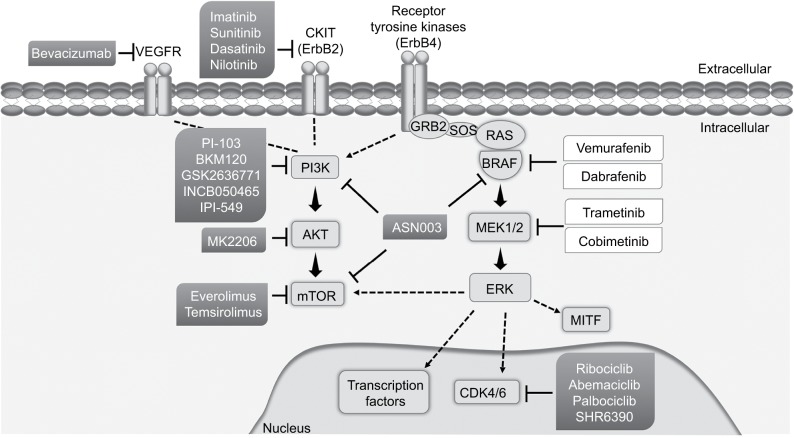
Figure 3.
Targeted therapies approved by FDA (in white – vemurafenib, dabrafenib, trametinib, and cobimetinib) or in trials (in gray – imatinib, sunitinib, dasatinib, nilotinib, bevacizumab, PI-103, BKM120, GSK2636771, INCB050465, IPI-549, MK2206, everolimus, temsirolimus, ribociclib, abemaciclib, palbociclib, SHR6390, and ASN003) for cutaneous melanoma treatment. Mutations on key signaling oncogenes, used as targets for melanoma therapy, are associated with melanoma cell proliferation, cell-cycle progression, and malignant phenotype. Melanoma patients may benefit from combined therapies, using two different targeted therapies or targeted therapy with adjuvant immune therapy or chemotherapy.
Abbreviations: FDA, US Food and Drug Administration; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; VEGFR, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; MITF, microphthalmia-associated transcription factor; CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase; P13K, phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase.