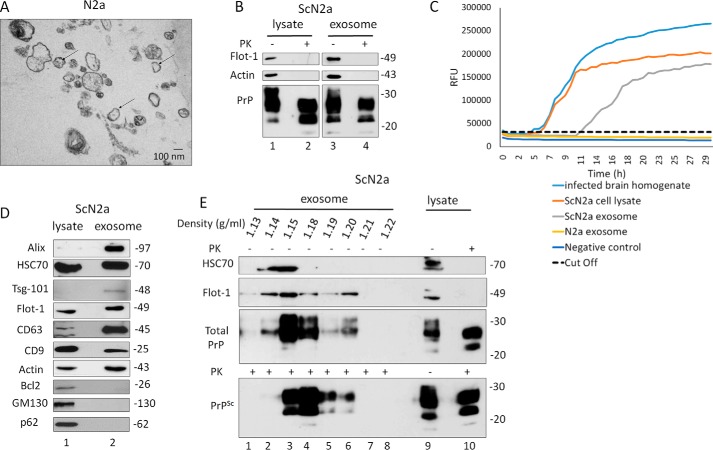
Figure 2.
Characterization of exosomes isolated from N2a/ScN2a cells. A, representative TEM of exosomes isolated from N2a culture medium shows a population of vesicles of 100 nm in diameter (some denoted by black arrows). Scale bar, 100 nm. B, immunoblot of ScN2a cell lysate and exosome preparations probed for total PrP (−PK) and PrPSc (+PK) (anti-PrP mAb 4H11). Flotillin-1 (Flot-1) was used as exosome marker. Actin was used as loading control. C, RT-QuIC of N2a exosome, ScN2a exosome, ScN2a cell lysate, and 10% brain homogenate from terminally prion-sick mice (22L) or left unseeded (negative control). The average increase of thioflavin-T fluorescence of replicate wells is plotted as a function of time. The y axis represents RFU, and the x axis represents time in hours. D, immunoblot analysis of ScN2a cell lysate and exosomes isolated from ScN2a cell culture medium. Exosome preparation is positive for exosome markers Alix, HSC70, Tsg-101, flotillin-1, CD63, and CD9 and negative for mitochondrial marker Bcl2, Golgi marker GM130, and nuclear marker nucleoporin p62. Actin was used as loading control. E, ScN2a exosome pallet loaded on the top of a continuous sucrose gradient and ultracentrifuged. The fractions were analyzed by Western blotting and probed for HSC70, flotillin-1, and mAb 4H11 to detect total PrP and PrPSc. Lanes 9 and 10 are cell lysate before and after PK digestion, respectively.