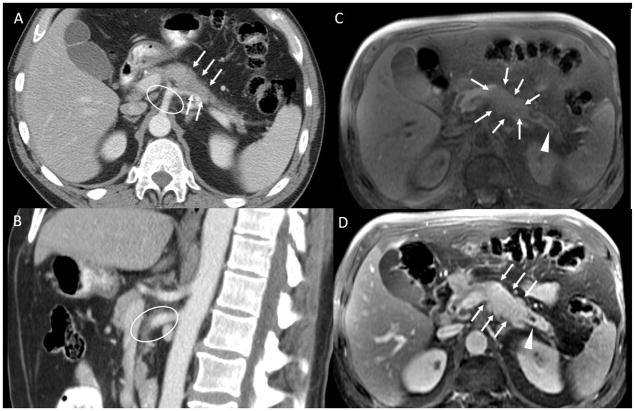
Figure 3.
A: axial CT pancreatic phase shows an isointense pancreatic body tumor, subtly visible in this scan and an encasement of splenic artery B: sagittal CT pancreatic phase at superior mesenteric artery and celiac axis level. C: axial MRI, spoiled Gradient echo fat-sat pre-contrast D: axial MRI, spoiled Gradient echo fat-sat post-contrast pancreatic-phase. The pancreatic head tumor is well depicted in T1 pre-contrast and post contrast images (white arrows in B and C), with a dilatation of the pancreatic duct (white arrowheads). There is mild hyperattenuating tissue surrounding the superior mesenteric artery and the celiac axis (white ellipses in A and C). This was reported as encasement of these arteries by the tumor on the outside report, interpreted by the surgeons as unresectable disease, and as inflammatory tissue on the second opinion report, interpreted by the surgeons as borderline resectable disease. The patient underwent neoadjuvant chemotherapy and was successfully resected.