Figure 2.
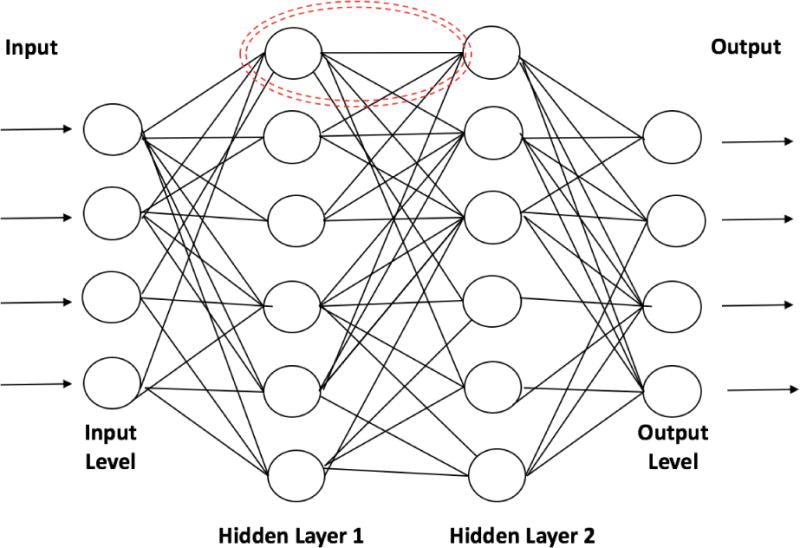
Artificial neural networks are composed of many computational units known as “neurons” (dotted red circle) that receive data inputs (similar to dendrites in biological neurons), perform calculations, and transmit output (similar to axons) to the next neuron. Input level neurons receive data while hidden layer neurons (many different hidden layers can be used) conduct the calculations necessary to analyze the complex relationships in the data. Hidden layer neurons then send the data to an output layer that provides the final version of the analysis for interpretation.
